Allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin expression with antisense oligonucleotides targeting the expanded CAG repeat
- PMID: 21028906
- PMCID: PMC2991413
- DOI: 10.1021/bi101208k
Allele-selective inhibition of mutant huntingtin expression with antisense oligonucleotides targeting the expanded CAG repeat
Abstract
Huntington's disease (HD) is a currently incurable neurodegenerative disease caused by the expansion of a CAG trinucleotide repeat within the huntingtin (HTT) gene. Therapeutic approaches include selectively inhibiting the expression of the mutated HTT allele while conserving function of the normal allele. We have evaluated a series of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeted to the expanded CAG repeat within HTT mRNA for their ability to selectively inhibit expression of mutant HTT protein. Several ASOs incorporating a variety of modifications, including bridged nucleic acids and phosphorothioate internucleotide linkages, exhibited allele-selective silencing in patient-derived fibroblasts. Allele-selective ASOs did not affect the expression of other CAG repeat-containing genes and selectivity was observed in cell lines containing minimal CAG repeat lengths representative of most HD patients. Allele-selective ASOs left HTT mRNA intact and did not support ribonuclease H activity in vitro. We observed cooperative binding of multiple ASO molecules to CAG repeat-containing HTT mRNA transcripts in vitro. These results are consistent with a mechanism involving inhibition at the level of translation. ASOs targeted to the CAG repeat of HTT provide a starting point for the development of oligonucleotide-based therapeutics that can inhibit gene expression with allelic discrimination in patients with HD.
Figures
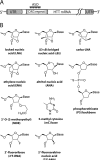



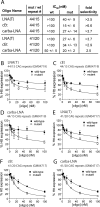



References
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Walker FO. Huntington's disease. Lancet. 2007;369:218–228. - PubMed
-
- MacDonald ME, Ambrose CM, Duyao MP, Myers RH, Lin C, Srinidhi L, Barnes G, Taylor SA, James M, Groot N, MacFarlane H, et al. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington's disease chromosomes. Cell. 1993;72:971–983. - PubMed
-
- Rubinsztein DC. Molecular biology of Huntington's disease (HD) and HD-like disorders. In: Pulst S, editor. Genetics of Movement Disorders. Academic Press; California: 2003. pp. 365–377.
-
- Rubinsztein DC, Leggo J, Coles R, Almqvist E, Biancalana V, Cassiman JJ, Chotai K, Connarty M, Crauford D, Curtis A, et al. Phenotypic characterization of individuals with 30–40 CAG repeats in the Huntington disease (HD) gene reveals HD cases with 36 repeats and apparently normal elderly individuals with 36–39 repeats. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996;59:16–22. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

