Mutation analysis of CCM1, CCM2 and CCM3 genes in a cohort of Italian patients with cerebral cavernous malformation
- PMID: 21029238
- PMCID: PMC8094256
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00441.x
Mutation analysis of CCM1, CCM2 and CCM3 genes in a cohort of Italian patients with cerebral cavernous malformation
Erratum in
- Brain Pathol. 2011 May;21(3):360
Abstract
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs) are vascular lesions of the CNS characterized by abnormally enlarged capillary cavities. CCMs can occur as sporadic or familial autosomal dominant form. Familial cases are associated with mutations in CCM1[K-Rev interaction trapped 1 (KRIT1)], CCM2 (MGC4607) and CCM3 (PDCD10) genes. In this study, a three-gene mutation screening was performed by direct exon sequencing, in a cohort of 95 Italian patients either sporadic or familial, as well as on their at-risk relatives. Sixteen mutations in 16 unrelated CCM patients were identified,nine mutations are novel: c.413T > C; c.601C > T; c.846 + 2T > G; c.1254delA; c.1255-4delGTA; c.1682-1683 delTA in CCM1; c.48A > G; c.82-83dupAG in CCM2; and c.395 + 1G > A in CCM3 genes [corrected].The samples, negative to direct exon sequencing, were investigated by MLPA to search for intragenic deletions or duplications. One deletion in CCM1 exon 18 was detected in a sporadic patient. Among familial cases 67% had a mutation in CCM1, 5.5% in CCM2, and 5.5% in CCM3, whereas in the remaining 22% no mutations were detected, suggesting the existence of either undetectable mutations or other CCM genes. This study represents the first extensive research program for a comprehensive molecular screening of the three known genes in an Italian cohort of CCM patients and their at-risk relatives.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

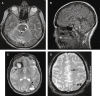


 = proband;
= proband; 
 = affected;
= affected; 
 = asymptomatic;
= asymptomatic; 
 = obligate carrier;
= obligate carrier; 
 = not known to be affected; M = mutation; WT = no mutation;
= not known to be affected; M = mutation; WT = no mutation; 
 = deceased.
= deceased.References
-
- Battistini S, Rocchi R, Cerase A (2007) Clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and genetic study of 5 Italian families with cerebral cavernous malformation. Arch Neurol 64:843–848. - PubMed
-
- Cartegni L, Chew SL, Krainer AR (2002) Listening to silence and understanding nonsense: exonic mutations that affect splicing. Nat Rev Genet 3:285–298. - PubMed
-
- Cau M, Loi M, Melis M, Congiu R, Loi A, Meloni C et al (2009) C329X in KRIT1 is a founder mutation among CCM patients in Sardinia. Eur J Med Genet 52:344–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

