Effect of vaccination on Bordetella pertussis strains, China
- PMID: 21029526
- PMCID: PMC3294513
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1611.100401
Effect of vaccination on Bordetella pertussis strains, China
Abstract
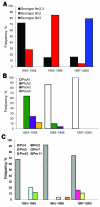
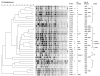
Whole-cell pertussis vaccine was introduced in China in the early 1960s. We used standard typing methods to compare 96 Bordetella pertussis isolates collected before and after introduction of vaccination, during 1953-2005. The following vaccine-type alleles of the pertussis toxin (ptx) gene were characteristic for all prevaccination strains: ptxA2, ptxA3, and ptxA4. The shift to ptxA1 occurred since 1963. All isolates collected since 1983 contained ptxA1. Pertactin (prn) allele 1, prn1, was predominant, although prn2 and prn3 have been detected since 2000. Serotypes fimbriae (Fim) 2 and Fim2,3 were found in all isolates collected before 1986. During 1997-2005, Fim3 became prevalent. Although changes in electrophoresis profiles over time were observed, the predominant profiles during 1997-2005 resembled those during the prevaccine era and those found in Europe before the 1990s. B. pertussis strains in China may differ from those in countries that have a long history of high vaccine coverage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antigenic divergence between Bordetella pertussis clinical isolates from Moscow, Russia, and vaccine strains.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Mar;14(3):234-8. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00294-06. Epub 2007 Jan 3. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17202309 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella pertussis vaccine strains and circulating isolates in Serbia.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 3;28(5):1188-92. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.036. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 19945417
-
Molecular epidemiology of Bordetella pertussis and analysis of vaccine antigen genes from clinical isolates from Shenzhen, China.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021 Aug 18;20(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12941-021-00458-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2021. PMID: 34407803 Free PMC article.
-
Bordetella pertussis fimbriae (Fim): relevance for vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Oct;13(10):1205-14. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.930667. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 25102891 Review.
-
[Genetic variability of Bordetella pertussis strains. Part I. Current knowledge].Przegl Epidemiol. 2003;57(1):181-92. Przegl Epidemiol. 2003. PMID: 12926327 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Identification of etiologic agents and clinical characteristics for patients suspected of having pertussis in a large Children's Hospital in China.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Sep;7(18):443. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.08.85. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31700879 Free PMC article.
-
Coping Strategies for Pertussis Resurgence.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Apr 24;11(5):889. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11050889. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct molecular typing of Bordetella pertussis from nasopharyngeal specimens in China in 2012-2013.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Jul;35(7):1211-4. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2655-3. Epub 2016 May 5. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27146879
-
Variation in Bordetella pertussis Susceptibility to Erythromycin and Virulence-Related Genotype Changes in China (1970-2014).PLoS One. 2015 Sep 25;10(9):e0138941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138941. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26406905 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of immunization programs on 11 childhood vaccine-preventable diseases in China: 1950-2018.Innovation (Camb). 2021 May 5;2(2):100113. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100113. eCollection 2021 May 28. Innovation (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34557762 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
