The long noncoding RNA, Jpx, is a molecular switch for X chromosome inactivation
- PMID: 21029862
- PMCID: PMC2994261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.09.049
The long noncoding RNA, Jpx, is a molecular switch for X chromosome inactivation
Abstract
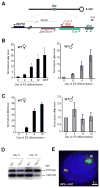
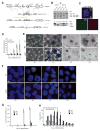
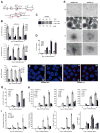
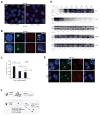
Once protein-coding, the X-inactivation center (Xic) is now dominated by large noncoding RNAs (ncRNA). X chromosome inactivation (XCI) equalizes gene expression between mammalian males and females by inactivating one X in female cells. XCI requires Xist, an ncRNA that coats the X and recruits Polycomb proteins. How Xist is controlled remains unclear but likely involves negative and positive regulators. For the active X, the antisense Tsix RNA is an established Xist repressor. For the inactive X, here, we identify Xic-encoded Jpx as an Xist activator. Jpx is developmentally regulated and accumulates during XCI. Deleting Jpx blocks XCI and is female lethal. Posttranscriptional Jpx knockdown recapitulates the knockout, and supplying Jpx in trans rescues lethality. Thus, Jpx is trans-acting and functions as ncRNA. Furthermore, ΔJpx is rescued by truncating Tsix, indicating an antagonistic relationship between the ncRNAs. We conclude that Xist is controlled by two RNA-based switches: Tsix for Xa and Jpx for Xi.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ariel M, Robinson E, McCarrey JR, Cedar H. Gamete-specific methylation correlates with imprinting of the murine Xist gene. Nat Genet. 1995;9:312–315. - PubMed
-
- Bacher CP, Guggiari M, Brors B, Augui S, Clerc P, Avner P, Eils R, Heard E. Transient colocalization of X-inactivation centres accompanies the initiation of X inactivation. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8:293–299. - PubMed
-
- Brockdorff N, Ashworth A, Kay GF, McCabe VM, Norris DP, Cooper PJ, Swift S, Rastan S. The product of the mouse Xist gene is a 15 kb inactive X-specific transcript containing no conserved ORF and located in the nucleus. Cell. 1992;71:515–526. - PubMed
-
- Brown CJ, Hendrich BD, Rupert JL, Lafreniere RG, Xing Y, Lawrence J, Willard HF. The human XIST gene: analysis of a 17 kb inactive X-specific RNA that contains conserved repeats and is highly localized within the nucleus. Cell. 1992;71:527–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

