Designing vaccines based on biology of human dendritic cell subsets
- PMID: 21029958
- PMCID: PMC2975953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.007
Designing vaccines based on biology of human dendritic cell subsets
Abstract
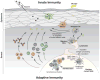
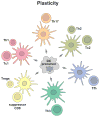
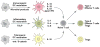
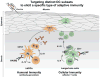
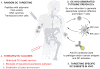
The effective vaccines developed against a variety of infectious agents, including polio, measles, and hepatitis B, represent major achievements in medicine. These vaccines, usually composed of microbial antigens, are often associated with an adjuvant that activates dendritic cells (DCs). Many infectious diseases are still in need of an effective vaccine including HIV, malaria, hepatitis C, and tuberculosis. In some cases, the induction of cellular rather than humoral responses may be more important because the goal is to control and eliminate the existing infection rather than to prevent it. Our increased understanding of the mechanisms of antigen presentation, particularly with the description of DC subsets with distinct functions, as well as their plasticity in responding to extrinsic signals, represent opportunities to develop novel vaccines. In addition, we foresee that this increased knowledge will permit us to design vaccines that will reprogram the immune system to intervene therapeutically in cancer, allergy, and autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Albert ML, Darnell JC, Bender A, Francisco LM, Bhardwaj N, Darnell RB. Tumor-specific killer cells in paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Nat Med. 1998;4:1321–1324. - PubMed
-
- Allan RS, Smith CM, Belz GT, van Lint AL, Wakim LM, Heath WR, Carbone FR. Epidermal viral immunity induced by CD8alpha+ dendritic cells but not by Langerhans cells. Science. 2003;301:1925–1928. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez D, Harder G, Fattouh R, Sun J, Goncharova S, Stampfli MR, Coyle AJ, Bramson JL, Jordana M. Cutaneous antigen priming via gene gun leads to skin-selective Th2 immune-inflammatory responses. J Immunol. 2005;174:1664–1674. - PubMed
-
- Antony PA, Piccirillo CA, Akpinarli A, Finkelstein SE, Speiss PJ, Surman DR, Palmer DC, Chan CC, Klebanoff CA, Overwijk WW, et al. CD8+ T cell immunity against a tumor/self-antigen Is augmented by CD4+ T helper cells and hindered by naturally occurring T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2005;174:2591–2601. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Appay V, Douek DC, Price DA. CD8+ T cell efficacy in vaccination and disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:623–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

