Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib
- PMID: 21030498
- PMCID: PMC2999638
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1588
Development of central nervous system metastases in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and somatic EGFR mutations treated with gefitinib or erlotinib
Abstract
Purpose: Gefitinib and erlotinib can penetrate into the central nervous system (CNS) and elicit responses in patients with brain metastases (BM) from non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, there are incomplete data about their impact on the development and control of CNS metastases.
Experimental design: Patients with stage IIIB/IV NSCLC with somatic EGFR mutations initially treated with gefitinib or erlotinib were identified. The cumulative risk of CNS progression was calculated using death as a competing risk.
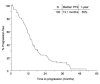
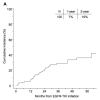
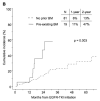
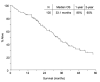
Results: Of the 100 patients, 19 had BM at the time of diagnosis of advanced NSCLC; 17 of them received CNS therapy before initiating gefitinib or erlotinib. Eighty-four patients progressed after a median potential follow-up of 42.2 months. The median time to progression was 13.1 months. Twenty-eight patients developed CNS progression, 8 of whom had previously treated BM. The 1- and 2-year actuarial risk of CNS progression was 7% and 19%, respectively. Patient age and EGFR mutation genotype were significant predictors of the development of CNS progression. The median overall survival for the entire cohort was 33.1 months.
Conclusions: Our data suggest a lower risk of CNS progression in patients with advanced NSCLC and somatic EGFR mutations initially treated with gefitinib or erlotinib than published rates of 40% in historical series of advanced NSCLC patients. Further research is needed to distinguish between the underlying rates of developing CNS metastases between NSCLC with and without EGFR mutations and the impact of gefitinib and erlotinib versus chemotherapy on CNS failure patterns in these patients.
©2010 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–49. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539–44. - PubMed
-
- Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3543–51. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM Classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2007;2:706–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

