The association between abnormal birth history and growth in children with CKD
- PMID: 21030583
- PMCID: PMC3022235
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08481109
The association between abnormal birth history and growth in children with CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: Poor linear growth is a well described complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This study evaluated whether abnormal birth history defined by low birth weight (LBW; <2500 g), prematurity (gestational age <36 weeks), small for gestational age (SGA; birth weight <10th percentile for gestational age), or intensive care unit (ICU) at birth were risk factors for poor growth outcomes in children with CKD.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Growth outcomes were quantified by age-sex-specific height and weight z-scores during 1393 visits from 426 participants of the Chronic Kidney Disease in Children Study, an observational cohort of children with CKD. Median baseline GFR was 42.9 ml/min per 1.73 m(2), 21% had a glomerular diagnosis, and 52% had CKD for ≥ 90% of their lifetime.
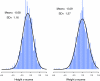
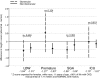
Results: A high prevalence of LBW (17%), SGA (14%), prematurity (12%), and ICU after delivery (40%) was observed. Multivariate analyses demonstrated a negative effect of LBW (-0.43 ± 0.14; P < 0.01 for height and -0.37 ± 0.16; P = 0.02 for weight) and of SGA (-0.29 ± 0.16; P = 0.07 for height and -0.41 ± 0.19; P = 0.03 for weight) on current height and weight. In children with glomerular versus nonglomerular diagnoses, the effect of SGA (-1.08 versus -0.18; P = 0.029) on attained weight was more pronounced in children with a glomerular diagnosis.
Conclusions: LBW and SGA are novel risk factors for short stature and lower weight percentiles in children with mild to moderate CKD independent of kidney function.
Figures

References
-
- Haffner D, Schaefer F, Nissel R, Wuhl E, Tonshoff B, Mehls O: Effect of growth hormone treatment on the adult height of children with chronic renal failure. German Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment in Chronic Renal Failure. N Engl J Med 343: 923–930, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Fine RN, Kohaut EC, Brown D, Perlman AJ: Growth after recombinant human growth hormone treatment in children with chronic renal failure: Report of a multicenter randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Genentech Cooperative Study Group. J Pediatr 124: 374–382, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Greenbaum LA, Del Rio M, Bamgbola F, Kaskel F: Rationale for growth hormone therapy in children with chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 11: 377–386, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Albertsson-Wikland K, Karlberg J: Postnatal growth of children born small for gestational age. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 423: 193–195, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- M01 RR0039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK82194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000039/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-66143/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-66116/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025008/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-DK-66174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK078737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082194/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK066143/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States

