Liver X receptor (LXR) regulates human adipocyte lipolysis
- PMID: 21030586
- PMCID: PMC3012995
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.179499
Liver X receptor (LXR) regulates human adipocyte lipolysis
Abstract
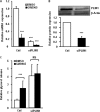
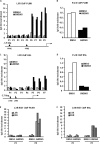
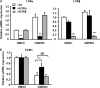
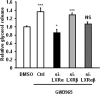
The Liver X receptor (LXR) is an important regulator of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in humans and mice. We have recently shown that activation of LXR regulates cellular fuel utilization in adipocytes. In contrast, the role of LXR in human adipocyte lipolysis, the major function of human white fat cells, is not clear. In the present study, we stimulated in vitro differentiated human and murine adipocytes with the LXR agonist GW3965 and observed an increase in basal lipolysis. Microarray analysis of human adipocyte mRNA following LXR activation revealed an altered gene expression of several lipolysis-regulating proteins, which was also confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR. We show that expression and intracellular localization of perilipin1 (PLIN1) and hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) are affected by GW3965. Although LXR activation does not influence phosphorylation status of HSL, HSL activity is required for the lipolytic effect of GW3965. This effect is abolished by PLIN1 knockdown. In addition, we demonstrate that upon activation, LXR binds to the proximal regions of the PLIN1 and HSL promoters. By selective knock-down of either LXR isoform, we show that LXRα is the major isoform mediating the lipolysis-related effects of LXR. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that activation of LXRα up-regulates basal human adipocyte lipolysis. This is at least partially mediated through LXR binding to the PLIN1 promoter and down-regulation of PLIN1 expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiotrophin-1 stimulates lipolysis through the regulation of main adipose tissue lipases.J Lipid Res. 2014 Dec;55(12):2634-43. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M055335. Epub 2014 Oct 28. J Lipid Res. 2014. PMID: 25351614 Free PMC article.
-
Serum amyloid A induces lipolysis by downregulating perilipin through ERK1/2 and PKA signaling pathways.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011 Dec;19(12):2301-9. doi: 10.1038/oby.2011.176. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2011. PMID: 21701568
-
Alpha-MSH signalling via melanocortin 5 receptor promotes lipolysis and impairs re-esterification in adipocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1831(7):1267-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.04.008. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24046867
-
The central role of perilipin a in lipid metabolism and adipocyte lipolysis.IUBMB Life. 2004 Jul;56(7):379-85. doi: 10.1080/15216540400009968. IUBMB Life. 2004. PMID: 15545214 Review.
-
Regulation of adipocyte lipolysis.Nutr Res Rev. 2014 Jun;27(1):63-93. doi: 10.1017/S095442241400002X. Epub 2014 May 28. Nutr Res Rev. 2014. PMID: 24872083 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs regulate human adipocyte lipolysis: effects of miR-145 are linked to TNF-α.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 24;9(1):e86800. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086800. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475180 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin 3C is a novel adipokine linked to extracellular matrix composition.Diabetologia. 2013 Aug;56(8):1792-801. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2931-z. Epub 2013 May 12. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23666167
-
Relationship between site-specific HSL phosphorylation and adipocyte lipolysis in obese women.Obes Facts. 2011;4(5):365-71. doi: 10.1159/000334036. Epub 2011 Oct 19. Obes Facts. 2011. PMID: 22166756 Free PMC article.
-
Delta-6 desaturase (Fads2) deficiency alters triacylglycerol/fatty acid cycling in murine white adipose tissue.J Lipid Res. 2023 Jun;64(6):100376. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100376. Epub 2023 Apr 19. J Lipid Res. 2023. PMID: 37085033 Free PMC article.
-
LXR is a negative regulator of glucose uptake in human adipocytes.Diabetologia. 2013 Sep;56(9):2044-54. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2954-5. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23765184
References
-
- Arner P., Langin D. (2007) Curr. Opin. Lipidology 18, 246–250 - PubMed
-
- Arner P. (2005) Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 19, 471–482 - PubMed
-
- Lafontan M., Langin D. (2009) Prog. Lipid Res. 48, 275–297 - PubMed
-
- Schweiger M., Schreiber R., Haemmerle G., Lass A., Fledelius C., Jacobsen P., Tornqvist H., Zechner R., Zimmermann R. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 40236–40241 - PubMed
-
- Ryden M., Jocken J., van Harmelen V., Dicker A., Hoffstedt J., Wiren M., Blomqvist L., Mairal A., Langin D., Blaak E. E., Arner P. (2007) Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol Metab. 292, 1847–1855 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

