Apical Na+-D-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) activity and protein abundance are expressed along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in the neonatal pig
- PMID: 21030609
- PMCID: PMC3025512
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00208.2010
Apical Na+-D-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) activity and protein abundance are expressed along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in the neonatal pig
Abstract
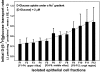
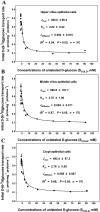
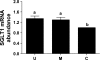
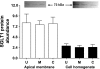
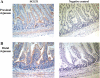
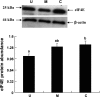
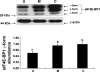
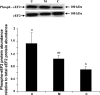
Gut apical Na(+)-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) activity is high at the birth and during suckling, thus contributing substantially to neonatal glucose homeostasis. We hypothesize that neonates possess high SGLT1 maximal activity by expressing apical SGLT1 protein along the intestinal crypt-villus axis via unique control mechanisms. Kinetics of SGLT1 activity in apical membrane vesicles, prepared from epithelial cells sequentially isolated along the jejunal crypt-villus axis from neonatal piglets by the distended intestinal sac method, were measured. High levels of maximal SGLT1 uptake activity were shown to exist along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in the piglets. Real-time RT-PCR analyses showed that SGLT1 mRNA abundance was lower (P < 0.05) by 30-35% in crypt cells than in villus cells. There were no significant differences in SGLT1 protein abundances on the jejunal apical membrane among upper villus, middle villus, and crypt cells, consistent with the immunohistochemical staining pattern. Higher abundances (P < 0.05) of total eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) protein and eIE4E-binding protein 1 γ-isoform in contrast to a lower (P < 0.05) abundance of phosphorylated (Pi) eukaryotic elongation factor 2 (eEF2) protein and the eEF2-Pi to total eEF2 abundance ratio suggest higher global protein translational efficiency in the crypt cells than in the upper villus cells. In conclusion, neonates have high intestinal apical SGLT1 uptake activity by abundantly expressing SGLT1 protein in the epithelia and on the apical membrane along the entire crypt-villus axis in association with enhanced protein translational control mechanisms in the crypt cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of apical Na(+)-L-glutamine co-transport activity, B(0)-system neutral amino acid co-transporter (B(0)AT1) and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in young pigs fed a liquid formula.Amino Acids. 2016 Jun;48(6):1491-508. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2210-7. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Amino Acids. 2016. PMID: 26984322
-
Expression of apical membrane L-glutamate transporters in neonatal porcine epithelial cells along the small intestinal crypt-villus axis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):G385-98. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00232.2003. Epub 2004 Mar 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15044176
-
Gradient for D-glucose and linoleic acid uptake along the crypt-villus axis of rabbit jejunal brush border membrane vesicles.Lipids. 1994 Feb;29(2):117-27. doi: 10.1007/BF02537151. Lipids. 1994. PMID: 8152345
-
Dietary and developmental regulation of intestinal sugar transport.Biochem J. 2001 Dec 1;360(Pt 2):265-76. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3600265. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11716754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal SGLT1 in metabolic health and disease.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):G887-98. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00068.2016. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27012770 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional evaluation of Bacillus licheniformis PF9 for its potential in controlling enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in weaned piglets.Transl Anim Sci. 2024 Apr 3;8:txae050. doi: 10.1093/tas/txae050. eCollection 2024. Transl Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38665217 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary thiazolidinedione supplementation on growth performance, intramuscular fat and related genes mRNA abundance in the longissimus dorsi muscle of finishing pigs.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013 Jul;26(7):1012-20. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12722. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 25049880 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a microencapsulated formula of organic acids and essential oils on nutrient absorption, immunity, gut barrier function, and abundance of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4 in weaned piglets challenged with E. coli F4.J Anim Sci. 2020 Sep 1;98(9):skaa259. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa259. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32780110 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Polyamines in Intestinal Development and Function in Piglets.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 19;14(8):1228. doi: 10.3390/ani14081228. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38672376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benzoic Acid Combined with Essential Oils Can Be an Alternative to the Use of Antibiotic Growth Promoters for Piglets Challenged with E. coli F4.Animals (Basel). 2020 Oct 28;10(11):1978. doi: 10.3390/ani10111978. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33126524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balen D, Ljubojevic M, Breljak D, Brzica H, Zlender V, Koepsell H, Sabolic I. Revised immunolocalization of the Na+-d-glucose cotransporter SGLT1 in rat organs with an improved antibody. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 295: C475–C489, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Byrkit DR. Statistics Today—A Comprehensive Introduction. Menlo Park, CA: Benjamin/Cummings, 1987
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

