CD11c/CD18 expression is upregulated on blood monocytes during hypertriglyceridemia and enhances adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- PMID: 21030716
- PMCID: PMC3038249
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.215434
CD11c/CD18 expression is upregulated on blood monocytes during hypertriglyceridemia and enhances adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
Abstract
Objective: Atherosclerosis is associated with monocyte adhesion to the arterial wall that involves integrin activation and emigration across inflamed endothelium. Involvement of β(2)-integrin CD11c/CD18 in atherogenesis was recently shown in dyslipidemic mice, which motivates our study of its inflammatory function during hypertriglyceridemia in humans.
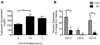
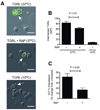
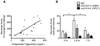
Methods and results: Flow cytometry of blood from healthy subjects fed a standardized high-fat meal revealed that at 3.5 hours postprandial, monocyte CD11c surface expression was elevated, and the extent of upregulation correlated with blood triglycerides. Monocytes from postprandial blood exhibited an increased light scatter profile, which correlated with elevated CD11c expression and uptake of lipid particles. Purified monocytes internalized triglyceride-rich lipoproteins isolated from postprandial blood through low-density lipoprotein-receptor-related protein-1, and this also elicited CD11c upregulation. Laboratory-on-a-chip analysis of whole blood showed that monocyte arrest on a vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) substrate under shear flow was elevated at 3.5 hours and correlated with blood triglyceride and CD11c expression. At 7 hours postprandial, blood triglycerides decreased and monocyte CD11c expression and arrest on VCAM-1 returned to fasting levels.
Conclusions: During hypertriglyceridemia, monocytes internalize lipids, upregulate CD11c, and increase adhesion to VCAM-1. These data suggest that analysis of monocyte inflammation may provide an additional framework for evaluating individual susceptibility to cardiovascular disease.
Figures


References
-
- Stary HC. Evolution and progression of atherosclerotic lesions in coronary arteries of children and young adults. Arteriosclerosis. 1989;9:I19–I32. - PubMed
-
- Strong JP, Malcom GT, McMahan CA, Tracy RE, Newman WP, III, Herderick EE, Cornhill JF for the Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth Research Group. Prevalence and Extent of Atherosclerosis in Adolescents and Young Adults: Implications for Prevention From the Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth Study. JAMA. 1999;281:727–735. - PubMed
-
- Khot UN, Khot MB, Bajzer CT, Sapp SK, Ohman EM, Brener SJ, Ellis SG, Lincoff AM, Topol EJ. Prevalence of conventional risk factors in patients with coronary heart disease. JAMA. 2003;290:898–904. - PubMed
-
- Cybulsky MI, Gimbrone MA., Jr Endothelial expression of a mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule during atherogenesis. Science. 1991;251:788–791. - PubMed
-
- Sakai A, Kume N, Nishi E, Tanoue K, Miyasaka M, Kita T. P-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 are focally expressed in aortas of hypercholesterolemic rabbits before intimal accumulation of macrophages and T lymphocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17:310–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL098839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA093373/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL098839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL086350/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047294/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AT000596/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK078847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL077281/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- HL079071/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078847/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL082689/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24-AT00596/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- HL082689/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

