Reduction of diphenyl diselenide and analogs by mammalian thioredoxin reductase is independent of their gluthathione peroxidase-like activity: a possible novel pathway for their antioxidant activity
- PMID: 21030914
- PMCID: PMC6259470
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15117700
Reduction of diphenyl diselenide and analogs by mammalian thioredoxin reductase is independent of their gluthathione peroxidase-like activity: a possible novel pathway for their antioxidant activity
Abstract
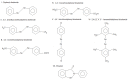
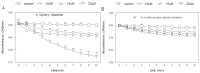
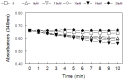
Since the successful use of the organoselenium drug ebselen in clinical trials for the treatment of neuropathological conditions associated with oxidative stress, there have been concerted efforts geared towards understanding the precise mechanism of action of ebselen and other organoselenium compounds, especially the diorganyl diselenides such as diphenyl diselenide, and its analogs. Although the mechanism of action of ebselen and other organoselenium compounds has been shown to be related to their ability to generally mimic native glutathione peroxidase (GPx), only ebselen however has been shown to serve as a substrate for the mammalian thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), demonstrating another component of its pharmacological mechanisms. In fact, there is a dearth of information on the ability of other organoselenium compounds, especially diphenyl diselenide and its analogs, to serve as substrates for the mammalian enzyme thioredoxin reductase. Interestingly, diphenyl diselenide shares several antioxidant and neuroprotective properties with ebselen. Hence in the present study, we tested the hypothesis that diphenyl diselenide and some of its analogs (4,4'-bistrifluoromethyldiphenyl diselenide, 4,4'-bismethoxy-diphenyl diselenide, 4.4'-biscarboxydiphenyl diselenide, 4,4'-bischlorodiphenyl diselenide, 2,4,6,2',4',6'-hexamethyldiphenyl diselenide) could also be substrates for rat hepatic TrxR. Here we show for the first time that diselenides are good substrates for mammalian TrxR, but not necessarily good mimetics of GPx, and vice versa. For instance, bis-methoxydiphenyl diselenide had no GPx activity, whereas it was a good substrate for reduction by TrxR. Our experimental observations indicate a possible dissociation between the two pathways for peroxide degradation (either via substrate for TrxR or as a mimic of GPx). Consequently, the antioxidant activity of diphenyl diselenide and analogs can be attributed to their capacity to be substrates for mammalian TrxR and we therefore conclude that subtle changes in the aryl moiety of diselenides can be used as tool for dissociation of GPx or TrxR pathways as mechanism triggering their antioxidant activities.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diphenyl diselenide and analogs are substrates of cerebral rat thioredoxin reductase: a pathway for their neuroprotective effects.Neurosci Lett. 2011 Sep 26;503(1):1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.07.050. Epub 2011 Aug 4. Neurosci Lett. 2011. PMID: 21839146
-
Diphenyl diselenide protects against methylmercury-induced inhibition of thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase in human neuroblastoma cells: a comparison with ebselen.J Appl Toxicol. 2017 Sep;37(9):1073-1081. doi: 10.1002/jat.3458. Epub 2017 Apr 6. J Appl Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28383113
-
Diselenoamino acid derivatives as GPx mimics and as substrates of TrxR: in vitro and in silico studies.Org Biomol Chem. 2018 May 23;16(20):3777-3787. doi: 10.1039/c8ob00451j. Org Biomol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29737350
-
Selenocysteine in mammalian thioredoxin reductase and application of ebselen as a therapeutic.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 Nov 1;127:238-247. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.05.081. Epub 2018 May 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29807162 Review.
-
Ebselen: a thioredoxin reductase-dependent catalyst for alpha-tocopherol quinone reduction.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005 Sep 1;207(2 Suppl):103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.02.022. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15979675 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Substitution on Cytotoxicity of Diphenyl Ditelluride in Cultured Vascular Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 29;22(19):10520. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910520. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638861 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-picolylamide-based diselenides with non-bonded interactions.Molecules. 2015 Jun 1;20(6):10095-109. doi: 10.3390/molecules200610095. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 26039333 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of diphenyl diselenide on ischemia and reperfusion-induced cerebral injury: involvement of oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines.Neurochem Res. 2012 Oct;37(10):2249-58. doi: 10.1007/s11064-012-0853-7. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Neurochem Res. 2012. PMID: 22846969
-
Antioxidant activity of β-selenoamines and their capacity to mimic different enzymes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2012 Jun;365(1-2):85-92. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1246-6. Epub 2012 Feb 7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22311601
-
New therapeutic approach: diphenyl diselenide reduces mitochondrial dysfunction in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 11;8(12):e81961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0081961. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24349162 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

