A novel antiangiogenic peptide derived from hepatocyte growth factor inhibits neovascularization in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 21031024
- PMCID: PMC2956696
A novel antiangiogenic peptide derived from hepatocyte growth factor inhibits neovascularization in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Purpose: To study the antiangiogenic activity of two small peptides (H-RN and H-FT) derived from the hepatocyte growth factor kringle 1 domain (HGF K1) using in vitro and in vivo assays.
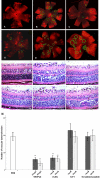
Methods: RF/6A rhesus macaque choroid-retina endothelial cells were used for in vitro studies. The inhibiting effect of two peptides on a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-stimulated cell proliferation, cell migration, and endothelial cell tube formation were investigated. For in vivo assays, the antiangiogenic activity of H-RN and H-FT in the chick chorioallantoic membrane model (CAM) and a mice oxygen-induced retinopathy model (OIR) were studied. A recombinant mouse VEGF-neutralizing antibody, bevacizumab, and a scrambled peptide were used as two control groups in separate studies.
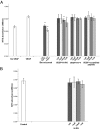
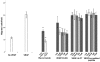
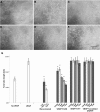
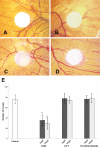
Results: H-RN effectively inhibited VEGF-stimulated RF/6A cell proliferation, migration, and tube formation on Matrigel™, while H-FT did not. H-RN was also able to inhibit angiogenesis when applied to the CAM, and had antineovascularization activity in the retinal neovascularization of a mouse OIR model when administrated as an intravitreous injection. The antiangiogenic activity of H-RN was not as strong as that of VEGF antibodies. The H-FT and scrambled peptide had no such activity.
Conclusions: H-RN, a new peptide derived from the HGF K1 domain, was shown to have antiangiogenic activity in vitro and in vivo. It may lead to new potential drug discoveries and the development of new treatments for pathological retinal angiogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
H-RN, a peptide derived from hepatocyte growth factor, inhibits corneal neovascularization by inducing endothelial apoptosis and arresting the cell cycle.BMC Cell Biol. 2013 Feb 24;14:8. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-14-8. BMC Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23433118 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Peptide NT/K-CFY Derived from Kringle Structure of Neurotrypsin Inhibits Neovascularization.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Oct;46(10):1551-1558. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2021.1907417. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33870816
-
Inhibition of pathological corneal neovascularization by a small peptide derived from human apolipoprotein (a) Kringle V.Cornea. 2014 Apr;33(4):405-13. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000032. Cornea. 2014. PMID: 24452210
-
A Novel Small Peptide H-KI20 Inhibits Retinal Neovascularization Through the JNK/ATF2 Signaling Pathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Jan 4;62(1):16. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.1.16. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33439229 Free PMC article.
-
Antiangiogenic Activity of Flavonoids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Molecules. 2020 Oct 14;25(20):4712. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204712. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33066630 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
17-Alpha-estradiol ameliorating oxygen-induced retinopathy in a murine model.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012 Jul;56(4):407-15. doi: 10.1007/s10384-012-0136-5. Epub 2012 May 15. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012. PMID: 22581453
-
Ritonavir inhibits HIF-1α-mediated VEGF expression in retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro.Eye (Lond). 2014 Jan;28(1):93-101. doi: 10.1038/eye.2013.240. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Eye (Lond). 2014. PMID: 24202050 Free PMC article.
-
Kallistatin inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of gastric cancer by downregulating VEGF-C expression and secretion.Gastric Cancer. 2018 Jul;21(4):617-631. doi: 10.1007/s10120-017-0787-5. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Gastric Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29243194
-
A Critical Analysis of the Available In Vitro and Ex Vivo Methods to Study Retinal Angiogenesis.J Ophthalmol. 2017;2017:3034953. doi: 10.1155/2017/3034953. Epub 2017 Aug 7. J Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28848677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel peptide specifically binding to VEGF receptor suppresses angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017 May 12;2:17010. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2017.10. eCollection 2017. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2017. PMID: 29263914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frank RN. Diabetic retinopathy. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:48–58. - PubMed
-
- Lala-Gitteau E, Majzoub S, Saliba E, Pisella PJ. Epidemiology for retinopathy of prematurity: risk factors in the Tours hospital. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2007;30:366–73. - PubMed
-
- Good WV, Hardy RJ. The multicenter study of Early Treatment for Retinopathy of Prematurity (ETROP). Ophthalmology. 2001;108:1013–4. - PubMed
-
- Smith LE. Pathogenesis of retinopathy of prematurity. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2004;14:S140–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
