A Novel LMNA Mutation Causes Altered Nuclear Morphology and Symptoms of Familial Partial Lipodystrophy (Dunnigan Variety) with Progeroid Features
- PMID: 21031082
- PMCID: PMC2957848
- DOI: 10.1159/000320166
A Novel LMNA Mutation Causes Altered Nuclear Morphology and Symptoms of Familial Partial Lipodystrophy (Dunnigan Variety) with Progeroid Features
Abstract
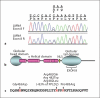
Dunnigan-type partial lipodystrophy (familial partial lipodystrophy, Dunnigan variety, FPLD2) can be caused by LMNA mutations. We identified a novel heterozygous LMNA mutation, P485R, in a patient referred to the International Registry of Werner Syndrome because of features consistent with that of progeroid disorder but who was wild type at the WRN locus. The novel mutation is located 2 amino acids away from the canonical FPLD mutations in exon 8 of the LMNA gene. Immunocytochemical analysis revealed abnormal nuclear morphology characteristic of laminopathies within primary fibroblast cultures, but not in a lymphoblastoid cell line, in keeping with previous observations. Our findings indicate that FPLD2 should be considered in the differential diagnosis of the Werner syndrome.
Figures

References
-
- Broers JL, Ramaekers FC, Bonne G, Yaou RB, Hutchison CJ. Nuclear lamins: laminopathies and their role in premature ageing. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:967–1008. - PubMed
-
- Cao H, Hegele RA. Nuclear lamin A/C R482Q mutation in Canadian kindreds with Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:109–112. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Lee L, Kudlow BA, Dos Santos HG, Sletvold O, et al. LMNA mutations in atypical Werner's syndrome. Lancet. 2003;362:440–445. - PubMed
-
- Dunnigan MG, Cochrane MA, Kelly A, Scott JW. Familial lipoatrophic diabetes with dominant transmission. A new syndrome. Q J Med. 1974;43:33–48. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

