Clinical and urodynamic significance of morphological differences in intravesical prostatic protrusion
- PMID: 21031089
- PMCID: PMC2963782
- DOI: 10.4111/kju.2010.51.10.694
Clinical and urodynamic significance of morphological differences in intravesical prostatic protrusion
Abstract
Purpose: The objectives of this study were to evaluate whether morphologic differences correlated with urodynamic and clinical characteristics in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) with intravesical prostatic protrusion (IPP) of trilobar or bilobar adenoma.
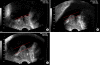
Materials and methods: Between January 2008 and June 2009, 72 male patients who had undergone transurethral resection (TUR) owing to BPH with IPP were included in this study. They underwent preoperative urodynamic studies, the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS)/quality of life (QoL), maximal flow rate (Qmax), post-voiding residual urine volume (PVR), transrectal ultrasonography (TRUS), and serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measurement. The patients were classified into 2 groups (the trilobar and bilobar adenoma groups) on the basis of video findings during the TUR operation.
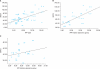
Results: The trilobar and bilobar adenoma groups consisted of 37 patients and 35 patients, respectively. The Mean±SD IPP, prostate volume (PV), and transition zone volume of the trilobar and bilobar adenoma groups were 11.8±5.2 mm and 9.0±3.8 mm (p=0.014), 81.1±25.8 g and 59.3±22.5 g (p<0.001), and 49.6±20.6 g and 34.8±19.4 g (p=0.003), respectively. The Mean±SD PSA, bladder contractility index (BCI), and bladder outlet obstruction index (BOOI) were 4.6±2.5 ng/ml and 3.5±1.7 ng/ml (p=0.042), 119.8±33.4 and 87.7±24.4 (p<0.001), and 62.6±29.5 and 44.6±20.4 (p=0.005), respectively. There were no significant differences in IPSS/QoL, Qmax, PVR, acute urinary retention, or detrusor overactivity in the 2 groups.
Conclusions: IPP has two morphologic types of trilobar or bilobar enlargement. The PV, BOOI, and BCI were significantly smaller in the bilobar adenoma group than in the trilobar adenoma group.
Keywords: Prostatic hyperplasia; Ultrasonography; Urodynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Lim KB, Ho H, Foo KT, Wong MY, Fook-Chong S. Comparison of intravesical prostatic protrusion, prostate volume and serum prostatic-specific antigen in the evaluation of bladder outlet obstruction. Int J Urol. 2006;13:1509–1513. - PubMed
-
- Chung HY, Han DS, Jang YS, Song KH. The influences of bladder outlet obstruction on improvement of storage symptoms in patients who underwent transurethral resection of prostate. Korean J Urol. 2008;49:912–916.
-
- Abrams P. Bladder outlet obstruction index, bladder contractility index and bladder voiding efficiency: three simple indices to define bladder voiding function. BJU Int. 1999;84:14–15. - PubMed
-
- Jung YS, Hwang TK, Kim JC. The outcome and satisfaction of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia following transurethral resection of the prostate according to urodynamic obstruction and the bladder function. Korean J Urol. 2007;48:965–970.
-
- Chia SJ, Heng CT, Chan SP, Foo KT. Correlation of intravesical prostatic protrusion with bladder outlet obstruction. BJU Int. 2003;91:371–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

