Diphosphoinositol polyphosphates: what are the mechanisms?
- PMID: 21035493
- PMCID: PMC3507380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2010.09.008
Diphosphoinositol polyphosphates: what are the mechanisms?
Abstract
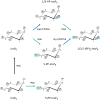
In countries where adulthood is considered to be attained at age eighteen, 2011 can be the point at which the diphosphoinositol polyphosphates might formally be described as "coming of age", since these molecules were first fully defined in 1993 (Menniti et al., 1993; Stephens et al., 1993b). But from a biological perspective, these polyphosphates cannot quite be considered to have matured into the status of being independently-acting intracellular signals. This review has discussed several of the published proposals for mechanisms by which the diphosphoinositol polyphosphates might act. We have argued that all of these hypotheses need further development.We also still do not know a single molecular mechanism by which a change in the levels of a particular diphosphoinositol polyphosphate can be controlled. Yet, despite all these gaps in our understanding, there is an enduring anticipation that these molecules have great potential in the signaling field. Reflecting our expectations of all teenagers, it should be our earnest hope that in the near future the diphosphoinositol polyphosphates will finally grow up.
Figures
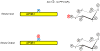
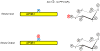
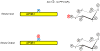
References
-
- Alfieri RR, Petronini PG. Hyperosmotic stress response: comparison with other cellular stresses. Pflugers Arch. 2007;454:173–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

