Measurement of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) activity in humans: validity of leukocyte p-MBS/t-MBS in comparison with vascular response to fasudil
- PMID: 21035804
- PMCID: PMC3807089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.10.005
Measurement of Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) activity in humans: validity of leukocyte p-MBS/t-MBS in comparison with vascular response to fasudil
Abstract
Background: Rho-associated kinases (ROCKs) have been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. It is clinically important to estimate the degree of ROCK activity in humans. The purpose of this study was to confirm the validity of a leukocyte ROCK parameter as an index of ROCK activity in comparison with vascular response to a ROCK inhibitor.
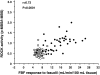
Methods and results: We evaluated the ratio of phospho myosin-binding subunit (p-MBS) on myosin light-chain phosphatase to total MBS in peripheral leukocytes by Western blot analysis and forearm blood flow (FBF) response to the ROCK inhibitor fasudil using strain-gauge plethysmography in 36 healthy subjects and 39 patients with cardiovascular diseases. Fasudil (3, 10, 30μg/min) was infused intra-arterially for 5min at each dose. Leukocyte p-MBS/total-MBS was higher in cardiovascular diseases than in healthy subjects (0.97±0.37 vs. 0.51±0.14; P=0.002). Fasudil increased FBF from 4.9±1.2 to 14.5±5.7mL/min/100mL tissue (P<0.0001) in patients with cardiovascular diseases, while fasudil did not alter FBF in healthy subjects. There was a significant relationship between leukocyte p-MBS/total-MBS and maximal FBF response to fasudil in all subjects (r=0.72, P<0.0001). There was also a significant correlation between p-MBS/total-MBS and maximal FBF response to fasudil in patients with cardiovascular diseases (r=0.59, P<0.0001). In healthy subjects, there was no significant correlation between the two parameters.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that assessment of leukocyte ROCK activity is minimally invasive and does not require pharmacologic intervention using ROCK inhibitors. Leukocyte p-MBS/total-MBS may be useful for evaluating ROCK activity in a clinical setting.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Smoking, endothelial function, and Rho-kinase in humans.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005 Dec;25(12):2630-5. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000189304.32725.bd. Epub 2005 Oct 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005. PMID: 16210569
-
Rho-associated kinase activity, endothelial function, and cardiovascular risk factors.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011 Oct;31(10):2353-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.227892. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011. PMID: 21737782 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of rho-associated kinase and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of aortic stiffness.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007 Feb 13;49(6):698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.06.082. Epub 2007 Jan 26. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17291936 Free PMC article.
-
Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology: the effect of fasudil.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;62(4):341-54. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3182a3718f. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23921309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of clinical efficacy of fasudil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2012 Aug;7(2):100-4. doi: 10.2174/157489012801227238. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22670803 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-1 prevents high-fat diet-induced endothelial permeability in apoE knock-out mice.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Jun;378(1-2):153-9. doi: 10.1007/s11010-013-1606-x. Epub 2013 Mar 7. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23467882 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor Sp1 Promotes the Expression of Porcine ROCK1 Gene.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 15;17(1):112. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010112. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784181 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cardioprotective mechanism of exogenous nitric oxide: inhibition of Rho-associated kinase activity.Hypertens Res. 2015 Jul;38(7):461-2. doi: 10.1038/hr.2015.61. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Hypertens Res. 2015. PMID: 25902902 No abstract available.
-
Effects and mechanism of moderate aerobic exercise on impaired fasting glucose improvement.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Dec 2;14:157. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0117-z. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26630989 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fasudil decreases lesion burden in a murine model of cerebral cavernous malformation disease.Stroke. 2012 Feb;43(2):571-4. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.625467. Epub 2011 Oct 27. Stroke. 2012. PMID: 22034008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature. 1997;389:990–994. - PubMed
-
- Hall A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279:509–514. - PubMed
-
- Takemoto M, Sun J, Hiroki J, Shimokawa H, Liao JK. Rho-kinase mediates hypoxia-induced downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 2002;106:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Laufs U, Liao JK. Post-transcriptional regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mRNA stability by Rho GTPase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:24266–24271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

