Prediction of ESRD and death among people with CKD: the Chronic Renal Impairment in Birmingham (CRIB) prospective cohort study
- PMID: 21035932
- PMCID: PMC2991589
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.07.016
Prediction of ESRD and death among people with CKD: the Chronic Renal Impairment in Birmingham (CRIB) prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Validated prediction scores are required to assess the risks of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and death in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Study design: Prospective cohort study with validation in a separate cohort.
Setting & participants: Cox regression was used to assess the relevance of baseline characteristics to risk of ESRD (mean follow-up, 4.1 years) and death (mean follow-up, 6.0 years) in 382 patients with stages 3-5 CKD not initially on dialysis therapy in the Chronic Renal Impairment in Birmingham (CRIB) Study. Resultant risk prediction equations were tested in a separate cohort of 213 patients with CKD (the East Kent cohort).
Factors: 44 baseline characteristics (including 30 blood and urine assays).
Outcomes: ESRD and all-cause mortality.
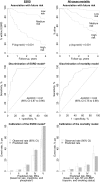
Results: In the CRIB cohort, 190 patients reached ESRD (12.1%/y) and 150 died (6.5%/y). Each 30% lower baseline estimated glomerular filtration rate was associated with a 3-fold higher ESRD rate and a 1.3-fold higher death rate. After adjustment for each other, only baseline creatinine level, serum phosphate level, urinary albumin-creatinine ratio, and female sex remained strongly (P < 0.01) predictive of ESRD. For death, age, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, troponin T level, and cigarette smoking remained strongly predictive of risk. Using these factors to predict outcomes in the East Kent cohort yielded an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ie, C statistic) of 0.91 (95% CI, 0.87-0.96) for ESRD and 0.82 (95% CI, 0.75-0.89) for death.
Limitations: Other important factors may have been missed because of limited study power.
Conclusions: Simple laboratory measures of kidney and cardiac function plus age, sex, and smoking history can be used to help identify patients with CKD at highest risk of ESRD and death. Larger cohort studies are required to further validate these results.
Copyright © 2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

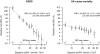
References
-
- Coresh J., Selvin E., Stevens L.A. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA. 2007;298:2038–2047. - PubMed
-
- Stevens P.E., O'Donoghue D.J., de Lusignan S. Chronic kidney disease management in the United Kingdom: NEOERICA project results. Kidney Int. 2007;72:92–99. - PubMed
-
- Tonelli M., Wiebe N., Culleton B. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2034–2047. - PubMed
-
- O'Hare A.M., Choi A.I., Bertenthal D. Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:2758–2765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

