A novel dithiocarbamate analogue with potentially decreased ALDH inhibition has copper-dependent proteasome-inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing activity in human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 21035945
- PMCID: PMC3671753
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2010.09.010
A novel dithiocarbamate analogue with potentially decreased ALDH inhibition has copper-dependent proteasome-inhibitory and apoptosis-inducing activity in human breast cancer cells
Abstract
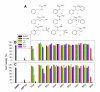
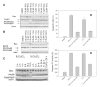
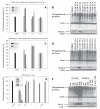
Dithiocarbamates are a class of sulfur-based metal-chelating compounds with various applications in medicine. We reported previously that certain members of dithiocarbamates, such as diethyldithiocarbamate, disulfiram (DSF) and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), were able to bind with tumor cellular copper to inhibit tumor growth through the inhibition of proteasome activity and induction of cancer cell apoptosis. Since the DSF is an irreversible inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), its ALDH-inhibitory activity might potentially affect its usefulness as an anti-cancer drug. For the purpose of selecting potent anti-cancer compounds that are not ALDH inhibitors and mapping out preliminary structure-activity relationship trends for these novel compounds, we synthesized a series of PDTC analogues and chose three novel compounds to study their ALDH-inhibitory activity, proteasome-inhibitory activity as well as the cancer cell apoptosis-inducing activity. The results showed that compared to DSF, compound 9 has less ALDH inhibition activity, and the in vitro results also proved the positive effects of 9-Cu in proteasome inhibition and apoptosis induction in breast cancer cells, suggesting that 9 as a lead compound could be developed into a novel proteasome inhibitor anti-cancer drug.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

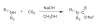
References
-
- Jacobson M, Weil M, Raff M. Programmed cell death review in animal development. Cell. 1997;88:347–354. - PubMed
-
- Thatte U, Dahanukar S. Apoptosis: clinical relevance and pharmacological manipulation. Drugs. 1997;54:511–532. - PubMed
-
- Song Z, Steller H. Death by design: mechanism and control of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9:49–52. - PubMed
-
- Gregoriadis G, Apostolidis N, Romanos A, Paradellis T. A comparative study of trace elements in normal and cancerous colorectal tissues. Cancer. 1983;52:508–519. - PubMed
-
- O’dell B. Biochemistry of copper. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1976;60:687–703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

