More membranes, more proteins: complex protein import mechanisms into secondary plastids
- PMID: 21036664
- PMCID: PMC3005297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.protis.2010.09.002
More membranes, more proteins: complex protein import mechanisms into secondary plastids
Abstract
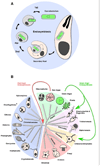
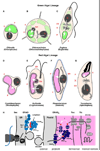
Plastids are found across the tree of life in a tremendous diversity of life forms. Surprisingly they are not limited to photosynthetic organisms but also found in numerous predators and parasites. An important reason for the pervasiveness of plastids has been their ability to move laterally and to jump from one branch of the tree of life to the next through secondary endosymbiosis. Eukaryotic algae have entered endosymbiotic relationships with other eukaryotes on multiple independent occasions. The descendants of these endosymbiotic events now carry complex plastids, organelles that are bound by three or even four membranes. As in all endosymbiotic organelles most of the symbiont's genes have been transferred to the host and their protein products have to be imported into the organelle. As four membranes might suggest, this is a complex process. The emerging mechanisms display a series of translocons that mirror the divergent ancestry of the membranes they cross. This review is written from the viewpoint of a parasite biologist and seeks to provide a brief overview of plastid evolution in particular for readers not already familiar with plant and algal biology and then focuses on recent molecular discoveries using genetically tractable Apicomplexa and diatoms.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adl SM, Simpson AG, Farmer MA, Andersen RA, Anderson OR, Barta JR, Bowser SS, Brugerolle G, Fensome RA, Fredericq S, James TY, Karpov S, Kugrens P, Krug J, Lane CE, Lewis LA, Lodge J, Lynn DH, Mann DG, McCourt RM, Mendoza L, Moestrup O, Mozley-Standridge SE, Nerad TA, Shearer CA, Smirnov AV, Spiegel FW, Taylor MF. The new higher level classification of eukaryotes with emphasis on the taxonomy of protists. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2005;52:399–451. - PubMed
-
- Archibald JM, Keeling PJ. Recycled plastids: a 'green movement' in eukaryotic evolution. Trends Genet. 2002;18:577–584. - PubMed
-
- Becker T, Qbadou S, Jelic M, Schleiff E. Let’s talk about.chloroplast import. Plant Biol. 2005;7:1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

