Zinc transporter 3 is involved in learned fear and extinction, but not in innate fear
- PMID: 21036893
- PMCID: PMC2981414
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.1962010
Zinc transporter 3 is involved in learned fear and extinction, but not in innate fear
Abstract
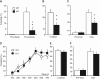
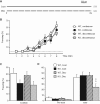
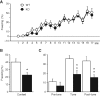
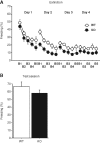
Synaptically released Zn²+ is a potential modulator of neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity in fear-conditioning pathways. Zinc transporter 3 (ZnT3) knock-out (KO) mice are well suited to test the role of zinc in learned fear, because ZnT3 is colocalized with synaptic zinc, responsible for its transport to synaptic vesicles, highly enriched in the amygdala-associated neural circuitry, and ZnT3 KO mice lack Zn²+ in synaptic vesicles. However, earlier work reported no deficiency in fear memory in ZnT3 KO mice, which is surprising based on the effects of Zn²+ on amygdala synaptic plasticity. We therefore reexamined ZnT3 KO mice in various tasks for learned and innate fear. The mutants were deficient in a weak fear-conditioning protocol using single tone-shock pairing but showed normal memory when a stronger, five-pairing protocol was used. ZnT3 KO mice were deficient in memory when a tone was presented as complex auditory information in a discontinuous fashion. Moreover, ZnT3 KO mice showed abnormality in trace fear conditioning and in fear extinction. By contrast, ZnT3 KO mice had normal anxiety. Thus, ZnT3 is involved in associative fear memory and extinction, but not in innate fear, consistent with the role of synaptic zinc in amygdala synaptic plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Armony JL, Servan-Schreiber D, Romanski LM, Cohen JD, LeDoux JE 1997. Stimulus generalization of fear responses: Effects of auditory cortex lesions in a computational model and in rats. Cereb Cortex 7: 157–165 - PubMed
-
- Bucci DJ, Phillips RG, Burwell RD 2000. Contributions of postrhinal and perirhinal cortex to contextual information processing. Behav Neurosci 114: 882–894 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
