Nf1-/- Schwann cell-conditioned medium modulates mast cell degranulation by c-Kit-mediated hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PMID: 21037083
- PMCID: PMC2993306
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100369
Nf1-/- Schwann cell-conditioned medium modulates mast cell degranulation by c-Kit-mediated hyperactivation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
Abstract
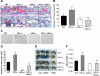
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genetic disorder and is characterized by both malignant and nonmalignant neurofibromas, which are composed of Schwann cells, degranulating mast cells, fibroblasts, and extracellular matrix. We and others have previously shown that hyperactivation of the c-Kit pathway in an Nf1 haploinsufficient microenvironment is required for both tumor formation and progression. Mast cells play a key role in both tumorigenesis and neoangiogenesis via the production of matrix metalloproteinases, heparin, and a range of different growth factors. In the present study, we show that tumorigenic Schwann cells derived from Nf1(-/-) embryos promote increased degranulation of Nf1(+/-) mast cells compared with wild-type mast cells via the secretion of the Kit ligand. Furthermore, we used genetic intercrosses as well as pharmacological agents to link the hyperactivation of the p21(Ras)-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway to the increased degranulation of Nf1(+/-) mast cells both in vitro and in vivo. These studies identify the p21(Ras)-PI3K pathway as a major regulator of the gain in Nf1(+/-) mast cell degranulation in neurofibromas. Collectively, these studies identify both c-Kit and PI3K as molecular targets that modulate mast cell functions in cases of NF1.
Figures
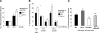
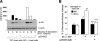
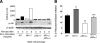
References
-
- Viskochil D, Buchberg AM, Xu G, Cawthon RM, Stevens J, Wolff RK, Culver M, Carey JC, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Deletions and a translocation interrupt a cloned gene at the neurofibromatosis type 1 locus. Cell. 1990;62:187–192. - PubMed
-
- Wallace MR, Marchuk DA, Andersen LB, Letcher R, Odeh HM, Saulino AM, Fountain JW, Brereton A, Nicholson J, Mitchell AL. Type 1 neurofibromatosis gene: identification of a large transcript disrupted in three NF1 patients. Science. 1990;249:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Coussens LM, Shapiro SD, Soloway PD, Werb Z. Models for gain-of-function and loss-of-function of MMPs. Transgenic and gene targeted mice. Methods Mol Biol. 2001;151:149–179. - PubMed
-
- Coussens LM, Fingleton B, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and tribulations. Science. 2002;295:2387–2392. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

