IgG1 is pathogenic in Leishmania mexicana infection
- PMID: 21037092
- PMCID: PMC2989177
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002484
IgG1 is pathogenic in Leishmania mexicana infection
Abstract
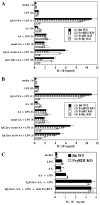
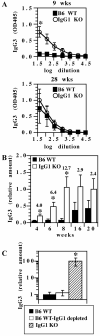
There are >2 million new cases of leishmaniasis annually, and no effective vaccine has been developed to prevent infection. In murine infection, Leishmania mexicana, which lives intracellularly in host macrophages, has developed pathways to hijack host IgG to induce a suppressive IL-10 response through FcγRs, the cell-surface receptors for IgG. To guide vaccine development away from detrimental Ab responses, which can accompany attempts to induce cell-mediated immunity, it is crucial to know which isotypes of IgG are pathogenic in this infection. We found that IgG1 and IgG2a/c induce IL-10 from macrophages in vitro equally well but through different FcγR subtypes: IgG1 through FcγRIII and IgG2a/c through FcγRI primarily, but also through FcγRIII. In sharp contrast, mice lacking IgG1 develop earlier and stronger IgG2a/c, IgG3, and IgM responses to L. mexicana infection and yet are more resistant to the infection. Thus, IgG1, but not IgG2a/c or IgG3, is pathogenic in vivo, in agreement with prior studies indicating that FcγRIII is required for chronic disease. This calls into question the assumption that macrophages, which should secrete IL-10 in response to IgG1 and IgG2a/c immune complexes, are the most important source of IL-10 generated by IgG-FcγR engagement in L. mexicana infection. Further investigations are required to better determine the cell type responsible for this immunosuppressive FcγRIII-induced IL-10 pathway and whether IgG2a/c is protective.
Figures
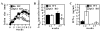

References
-
- World Health Organization Leishmaniasis. [Accessed: October 14, 2010]. 2005. Avalable at: http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/en/
-
- World Health Organization World Health Report: Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life. [Accessed: October 14, 2010]. 2002. Available at: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/whr02_en.pdf.
-
- Bryceson AD, Chulay JD, Ho M, Mugambii M, Were JB, Muigai R, Chunge C, Gachihi G, Meme J, Anabwani G. Visceral leishmaniasis unresponsive to antimonial drugs. I. Clinical and immunological studies. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985;79:700–704. e. al. - PubMed
-
- Sundar S, More DK, Singh MK, Singh VP, Sharma S, Makharia A, Kumar PC, Murray HW. Failure of pentavalent antimony in visceral leishmaniasis in India: report from the center of the Indian epidemic. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000;31:1104–1107. - PubMed
-
- Soto J, Toledo J, Vega J, Berman J. Short report: efficacy of pentavalent antimony for treatment of colombian cutaneous leishmaniasis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005;72:421–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

