Hypotonic swelling-induced activation of PKN1 mediates cell survival in cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 21037231
- PMCID: PMC3023260
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00232.2010
Hypotonic swelling-induced activation of PKN1 mediates cell survival in cardiac myocytes
Abstract
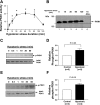
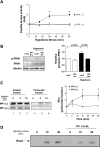
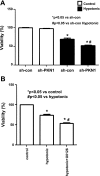
Hypotonic cell swelling in the myocardium is induced by pathological conditions, including ischemia-reperfusion, and affects the activities of ion transporters/channels and gene expression. However, the signaling mechanism activated by hypotonic stress (HS) is not fully understood in cardiac myocytes. A specialized protein kinase cascade, consisting of Pkc1 and MAPKs, is activated by HS in yeast. Here, we demonstrate that protein kinase N1 (PKN1), a serine/threonine protein kinase and a homolog of Pkc1, is activated by HS (67% osmolarity) within 5 min and reaches peak activity at 60 min in cardiac myocytes. Activation of PKN1 by HS was accompanied by Thr(774) phosphorylation and concomitant activation of PDK1, a potential upstream regulator of PKN1. HS also activated RhoA, thereby increasing interactions between PKN1 and RhoA. PP1 (10(-5) M), a selective Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor, significantly suppressed HS-induced activation of RhoA and PKN1. Constitutively active PKN1 significantly increased the transcriptional activity of Elk1-GAL4, an effect that was inhibited by dominant negative MEK. Overexpression of PKN1 significantly increased ERK phosphorylation, whereas downregulation of PKN1 inhibited HS-induced ERK phosphorylation. Downregulation of PKN1 and inhibition of ERK by U-0126 both significantly inhibited the survival of cardiac myocytes in the presence of HS. These results suggest that a signaling cascade, consisting of Src, RhoA, PKN1, and ERK, is activated by HS, thereby promoting cardiac myocyte survival.
Figures



References
-
- Aikawa R, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, Zou Y, Kudoh S, Zhu W, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y. Rho family small G proteins play critical roles in mechanical stress- induced hypertrophic responses in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 84: 458–466, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Mukai H, Ono Y, Chihara K, Matsui T, Hamajima Y, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Kaibuchi K. Identification of a putative target for Rho as the serine-threonine kinase protein kinase N. Science 271: 648–650, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Aoki H, Izumo S, Sadoshima J. Angiotensin II activates RhoA in cardiac myocytes:a critical role of RhoA in angiotensin II-induced premyofibril formation. Circ Res 81: 666–676, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong SC, Shivell LC, Ganote CE. Sarcolemmal blebs and osmotic fragility as correlates of irreversible ischemic injury in preconditioned isolated rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33: 149–160, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Atienza JM, Suh M, Xenarios I, Landgraf R, Colicelli J. Human ERK1 induces filamentous growth and cell wall remodeling pathways in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 275: 20638–20646, 2000 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

