Cadherin, alkaline phosphatase, and aminopeptidase N as receptors of Cry11Ba toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan in Aedes aegypti
- PMID: 21037295
- PMCID: PMC3019721
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01852-10
Cadherin, alkaline phosphatase, and aminopeptidase N as receptors of Cry11Ba toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan in Aedes aegypti
Abstract
Cry11Ba is one of the most toxic proteins to mosquito larvae produced by Bacillus thuringiensis. It binds Aedes aegypti brush border membrane vesicles (BBMV) with high affinity, showing an apparent dissociation constant (K(d)) of 8.2 nM. We previously reported that an anticadherin antibody competes with Cry11Ba binding to BBMV, suggesting a possible role of cadherin as a toxin receptor. Here we provide evidence of specific cadherin repeat regions involved in this interaction. Using cadherin fragments as competitors, a C-terminal fragment which contains cadherin repeat 7 (CR7) to CR11 competed with Cry11Ba binding to BBMV. This binding was also efficiently competed by the CR9, CR10, and CR11 peptide fragments. Moreover, we show CR11 to be an important region of interaction with Cry11Ba toxin. An alkaline phosphatase (AaeALP1) and an aminopeptidase-N (AaeAPN1) also competed with Cry11Ba binding to Ae. aegypti BBMV. Finally, we found that Cry11Ba and Cry4Ba share binding sites. Synthetic peptides corresponding to loops α8, β2-β3 (loop 1), β8-β9, and β10-β11 (loop 3) of Cry4Ba compete with Cry11Ba binding to BBMV, suggesting Cry11Ba and Cry4Ba have common sites involved in binding Ae. aegypti BBMV. The data suggest that three different Ae. aegypti midgut proteins, i.e., cadherin, AaeALP1, and AaeAPN1, are involved in Cry11Ba binding to Ae. aegypti midgut brush border membranes.
Figures


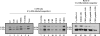


Similar articles
-
Aedes aegypti cadherin serves as a putative receptor of the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis.Biochem J. 2009 Nov 11;424(2):191-200. doi: 10.1042/BJ20090730. Biochem J. 2009. PMID: 19732034 Free PMC article.
-
A 104 kDa Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N is a putative receptor for the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Dec;43(12):1201-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2013.09.007. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24128608 Free PMC article.
-
A 106-kDa aminopeptidase is a putative receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxin in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae.Biochemistry. 2008 Oct 28;47(43):11263-72. doi: 10.1021/bi801181g. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18826260 Free PMC article.
-
AgCad2 cadherin in Anopheles gambiae larvae is a putative receptor of Cry11Ba toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. jegathesan.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Feb;43(2):153-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23231770
-
Role of Lectin in the Response of Aedes aegypti Against Bt Toxin.Front Immunol. 2022 May 13;13:898198. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.898198. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cry4Aa and Cry4Ba Mosquito-Active Toxins Utilize Different Domains in Binding to a Particular Culex ALP Isoform: A Functional Toxin Receptor Implicating Differential Actions on Target Larvae.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 21;14(10):652. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100652. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287921 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, expression and activity of ATP-binding protein in Bacillus thuringiensis toxicity modulation against Aedes aegypti.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jun 25;12(1):319. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3560-2. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31238963 Free PMC article.
-
Aedes cadherin receptor that mediates Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxicity is essential for mosquito development.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Feb 3;14(2):e0007948. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007948. eCollection 2020 Feb. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32012156 Free PMC article.
-
ABCC transporters mediate insect resistance to multiple Bt toxins revealed by bulk segregant analysis.BMC Biol. 2014 Jun 9;12:46. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-12-46. BMC Biol. 2014. PMID: 24912445 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of Aedes aegypti alkaline phosphatase ALP1 involved in the toxicity of Cry toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and jegathesan.Peptides. 2017 Dec;98:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2017.05.011. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Peptides. 2017. PMID: 28587836 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdul-Rauf, M., and D. J. Ellar. 1999. Mutations of loop 2 and loop 3 residues in domain II of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C delta-endotoxin affect insecticidal specificity and initial binding to Spodoptera littoralis and Aedes aegypti midgut membranes. Curr. Microbiol. 39:94-98. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Rauf, M., and D. J. Ellar. 1999. Toxicity and receptor binding properties of a Bacillus thuringiensis CryIC toxin active against both lepidoptera and diptera. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 73:52-58. - PubMed
-
- Bayyareddy, K., T. M. Andacht, M. A. Abdullah, and M. J. Adang. 2009. Proteomic identification of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis toxin Cry4Ba binding proteins in midgut membranes from Aedes (Stegomyia) aegypti Linnaeus (Diptera, Culicidae) larvae. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 39:279-286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

