Targeting of tumor radioiodine therapy by expression of the sodium iodide symporter under control of the survivin promoter
- PMID: 21037556
- PMCID: PMC3025317
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2010.66
Targeting of tumor radioiodine therapy by expression of the sodium iodide symporter under control of the survivin promoter
Abstract
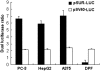
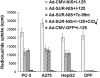
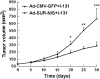
To test the feasibility of using the survivin promoter to induce specific expression of sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) in cancer cell lines and tumors for targeted use of radionuclide therapy, a recombinant adenovirus, Ad-SUR-NIS, that expressed the NIS gene under control of the survivin promoter was constructed. Ad-SUR-NIS mediating iodide uptake and cytotoxicity was performed in vitro. Scintigraphic, biodistribution and radioiodine therapy studies were performed in vivo. PC-3 (prostate); HepG2 (hepatoma) and A375 (melanoma) cancer cells all exhibited perchlorate-sensitive iodide uptake after infection with Ad-SUR-NIS, approximately 50 times higher than that of negative control Ad-CMV-GFP-infected cells. No significant iodide uptake was observed in normal human dental pulp fibroblast (DPF) cells after infection with Ad-SUR-NIS. Clonogenic assays demonstrated that Ad-SUR-NIS-infected cancer cells were selectively killed by exposure to (131)I. Ad-SUR-NIS-infected tumors show significant radioiodine accumulation (13.3 ± 2.85% ID per g at 2 h post-injection), and the effective half-life was 3.1 h. Moreover, infection with Ad-SUR-NIS in combination with (131)I suppressed tumor growth. These results indicate that expression of NIS under control of the survivin promoter can likely be used to achieve cancer-specific expression of NIS in many types of cancers. In combination with radioiodine therapy, this strategy is a possible method of cancer gene therapy.
Figures



References
-
- Dai G, Levy O, Carrasco N. Cloning and characterization of the thyroid iodide transporter. Nature. 1996;379:458–460. - PubMed
-
- De La Vieja A, Dohan O, Levy O, Carrasco N. Molecular analysis of the sodium/iodide symporter: impact on thyroid and extrathyroid pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1083–1105. - PubMed
-
- Spitzweg C, Heufelder AE, Morris JC. Thyroid iodine transport. Thyroid. 2000;10:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Smanik PA, Liu Q, Furminger TL, Ryu K, Xing S, Mazzaferri EL, et al. Cloning of the human sodium lodide symporter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996;226:339–345. - PubMed
-
- Spitzweg C, O'Connor MK, Bergert ER, Tindall DJ, Young CY, Morris JC. Treatment of prostate cancer by radioiodine therapy after tissue-specific expression of the sodium iodide symporter. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6526–6530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

