Rapid blue-light-mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells
- PMID: 21037589
- PMCID: PMC3059133
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.1524
Rapid blue-light-mediated induction of protein interactions in living cells
Abstract
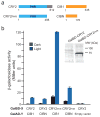
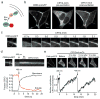
Dimerizers allowing inducible control of protein-protein interactions are powerful tools for manipulating biological processes. Here we describe genetically encoded light-inducible protein-interaction modules based on Arabidopsis thaliana cryptochrome 2 and CIB1 that require no exogenous ligands and dimerize on blue-light exposure with subsecond time resolution and subcellular spatial resolution. We demonstrate the utility of this system by inducing protein translocation, transcription and Cre recombinase-mediated DNA recombination using light.
Figures

References
-
- Spencer DM, Wandless TJ, Schreiber SL, Crabtree GR. Controlling signal transduction with synthetic ligands. Science. 1993;262:1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Bishop A, et al. Unnatural ligands for engineered proteins: new tools for chemical genetics. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:577–606. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu-Sato S, Huq E, Tepperman JM, Quail PH. A light-switchable gene promoter system. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:1041–1044. - PubMed
-
- Yazawa M, Sadaghiani AM, Hsueh B, Dolmetsch RE. Induction of protein-protein interactions in live cells using light. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:941–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

