Polymerase γ gene POLG determines the risk of sodium valproate-induced liver toxicity
- PMID: 21038416
- PMCID: PMC3841971
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23891
Polymerase γ gene POLG determines the risk of sodium valproate-induced liver toxicity
Abstract
Sodium valproate (VPA) is widely used throughout the world to treat epilepsy, migraine, chronic headache, bipolar disorder, and as adjuvant chemotherapy. VPA toxicity is an uncommon but potentially fatal cause of idiosyncratic liver injury. Rare mutations in POLG, which codes for the mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (polγ), cause Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome (AHS). AHS is a neurometabolic disorder associated with an increased risk of developing fatal VPA hepatotoxicity. We therefore set out to determine whether common genetic variants in POLG explain why some otherwise healthy individuals develop VPA hepatotoxicity. We carried out a prospective study of subjects enrolled in the Drug Induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN) from 2004 to 2008 through five US centers. POLG was sequenced and the functional consequences of VPA and novel POLG variants were evaluated in primary human cell lines and the yeast model system Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Heterozygous genetic variation in POLG was strongly associated with VPA-induced liver toxicity (odds ratio = 23.6, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 8.4-65.8, P = 5.1 × 10⁻⁷). This was principally due to the p.Q1236H substitution which compromised polγ function in yeast. Therapeutic doses of VPA inhibited human cellular proliferation and high doses caused nonapoptotic cell death, which was not mediated through mitochondrial DNA depletion, mutation, or a defect of fatty acid metabolism.
Conclusion: These findings implicate impaired liver regeneration in VPA toxicity and show that prospective genetic testing of POLG will identify individuals at high risk of this potentially fatal consequence of treatment.
Figures

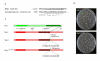
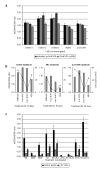
References
-
- Dreifuss FE, Langer DH, Moline KA, Maxwell JE. Valproic acid hepatic fatalities. II. US experience since 1984. Neurology. 1989 Feb;39(2 Pt 1):201–7. - PubMed
-
- Bryant AE, 3rd, Dreifuss FE. Valproic acid hepatic fatalities. III. U.S. experience since 1986. Neurology. 1996 Feb;46(2):465–9. - PubMed
-
- Gopaul S, Farrell K, Abbott F. Effects of age and polytherapy, risk factors of valproic acid (VPA) hepatotoxicity, on the excretion of thiol conjugates of (E)-2,4-diene VPA in people with epilepsy taking VPA. Epilepsia. 2003 Mar;44(3):322–8. - PubMed
-
- Naviaux RK, Nguyen KV. POLG mutations associated with Alpers’ syndrome and mitochondrial DNA depletion. Ann Neurol. 2004 May;55(5):706–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK065211/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083020/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065176/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2U01-DK065211-06/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR02984/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- GGP07019/TI_/Telethon/Italy
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01DK065193-04/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK083027/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065201/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065193/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR025747/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01-DK065238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DK062505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ULI RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025747/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024150/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- UL1 RR024986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK065184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK082992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
