Increased ethanol consumption and preference in mice lacking neurotensin receptor type 2
- PMID: 21039631
- PMCID: PMC3058519
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01326.x
Increased ethanol consumption and preference in mice lacking neurotensin receptor type 2
Abstract
Background: Neurotensin receptors (NTS) regulate a variety of the biological functions of neurotensin (NT) in the central nervous system. Although NT and neurotensin receptors type 1 (NTS1) are implicated in some of the behavioral effects of ethanol, the functional roles of neurotensin receptors type 2 (NTS2) in ethanol intoxication and consumption remain unknown. Here, we investigated behavioral effects mediated by NTS2 in response to ethanol, which are implicated in ethanol consumption and preference, using NTS2 null mice.
Method: First, we examined ethanol-induced locomotion, ataxia, hypnosis, and hypothermia in NTS2 null mice. Next, we measured ethanol consumption and preference in NTS2 null mice by giving them free choice between ethanol- and tap water-containing bottles. Then using a brain-permeable NT analog, NT69L, we examined the role of NTS2 in locomotor activity and ataxia. Finally, we examined the effect of NT69L on ethanol consumption and preference in NTS2 null mice.
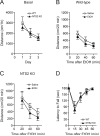
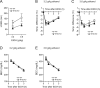
Results: We found that NTS2 null mice appear less sensitive to the acute hypnotic effects of ethanol and consumed more ethanol compared to wild-type littermates in a 2-bottle choice experiment, even though ethanol-induced locomotion, ataxia, and hypothermia were similar between genotypes. Interestingly, the administration of NT69L for 4 consecutive days significantly reduced alcohol consumption and preference in wild-type littermates as well as in NTS2 null mice.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that NTS2 regulates ethanol-induced hypnosis and ethanol consumption.
Copyright © 2010 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
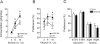
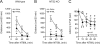

References
-
- Boudin H, Pelaprat D, Rostene W, Beaudet A. Cellular distribution of neurotensin receptors in rat brain: immunohistochemical study using an antipeptide antibody against the cloned high affinity receptor. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:76–89. - PubMed
-
- Boules M, Fredrickson P, Richelson E. Bioactive analogs of neurotensin: focus on CNS effects. Peptides. 2006;27:2523–2533. - PubMed
-
- Bowers BJ, Collins AC, Tritto T, Wehner JM. Mice lacking PKC gamma exhibit decreased anxiety. Behav Genet. 2000;30:111–121. - PubMed
-
- Caceda R, Kinkead B, Nemeroff CB. Neurotensin: role in psychiatric and neurological diseases. Peptides. 2006;27:2385–2404. - PubMed
-
- Carraway R, Leeman SE. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:6854–6861. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

