Atenolol blunts blood pressure increase during dynamic resistance exercise in hypertensives
- PMID: 21039760
- PMCID: PMC2997306
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03742.x
Atenolol blunts blood pressure increase during dynamic resistance exercise in hypertensives
Abstract
Aims: This study was conducted to determine whether atenolol was able to decrease BP level and mitigate BP increase during dynamic resistance exercise performed at three different intensities in hypertensives.
Methods: Ten essential hypertensives (systolic/diastolic BP between 140/90 and 160/105mmHg) were blindly studied after 6 weeks of placebo and atenolol. In each phase, volunteers executed, in a random order, three protocols of knee-extension exercises to fatigue: (i) one set at 100% of 1RM; (ii) three sets at 80% of 1RM; and (iii) three sets at 40% of 1RM. Intra-arterial radial blood pressure was measured throughout the protocols.
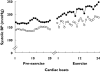
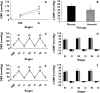
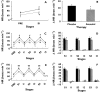
Results: Atenolol decreased systolic BP maximum values achieved during the three exercise protocols (100% = 186 ± 4 vs. 215 ± 7, 80% = 224 ± 7 vs. 247 ± 9 and 40% = 223 ± 7 vs. 252 ± 16mmHg, P < 0.05). Atenolol also mitigated an increase in systolic BP in the first set of exercises (100% =+38 ± 5 vs.+54 ± 9; 80% =+68 ± 11 vs. +84 ± 13 and 40% =+69 ± 7 vs.+84 ± 14, mmHg, P < 0.05). Atenolol decreased diastolic BP values and mitigated its increase during exercise performed at 100% of 1RM (126 ± 6 vs. 145 ± 6 and +41 ± 6 vs.+52 ± 6, mmHg, P < 0.05), but not at the other exercise intensities.
Conclusions: Atenolol was effective in both reducing systolic BP maximum values and mitigating BP increase during resistance exercise performed at different intensities in hypertensive subjects.
© 2010 The Authors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology © 2010 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Amlodipine reduces blood pressure during dynamic resistance exercise in hypertensive patients.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015 Feb;25(1):53-60. doi: 10.1111/sms.12152. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015. PMID: 24256097 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra-arterial blood pressure response in hypertensive subjects during low- and high-intensity resistance exercise.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2010 Mar;65(3):271-7. doi: 10.1590/S1807-59322010000300006. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2010. PMID: 20360917 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of rilmenidine and atenolol on mental stress, dynamic exercise and autonomic function in mild to moderate hypertension.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Dec;40(6):563-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1995.tb05801.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8703663 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A meta-analytical comparison of atenolol with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on arterial stiffness, peripheral blood pressure and heart rate in hypertensive patients.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39(5):421-426. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2016.1267188. Epub 2017 May 23. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28534649 Review.
-
Atenolol: differences in mode of action compared with other antihypertensives. An opportunity to identify features that influence outcome?Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(2):229-39. doi: 10.2174/138161207779313713. Curr Pharm Des. 2007. PMID: 17269930 Review.
Cited by
-
Blood pressure response to resistance training in hypertensive and normotensive older women.Clin Interv Aging. 2018 Apr 9;13:541-553. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S157479. eCollection 2018. Clin Interv Aging. 2018. PMID: 29674845 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Resistance Training on Muscle Quality Index, Muscle Strength, Functional Capacity, and Serum Immunoglobulin Levels between Obese and Non-obese Older Women.Int J Exerc Sci. 2021 Aug 1;14(7):707-726. doi: 10.70252/OIZW2471. eCollection 2021. Int J Exerc Sci. 2021. PMID: 34567383 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Pressure Increase in Hypertensive Individuals During Resistance Training Protocols With Equated Work to Rest Ratio.Front Physiol. 2020 Jun 29;11:481. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00481. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32714194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleck SJ, Kraemer WJ. Basic principles of resistance training and exercise prescription. In: Fleck SJ, Kraemer WJ, editors. Designing Resistance Training Programs. 3rd. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics; 2004. pp. 3–12.
-
- Pescatello LS, Franklin BA, Fagard R, Farquhar WB, Kelley GA, Ray CA. American colle-ge of sports medicine position stand. Exercise and hypertension. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004;36:533–53. - PubMed
-
- Bezucha GR, Lenser MC, Hanson PG, Nagle FJ. Comparison of hemodynamic responses to static and dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1982;53:1589–93. - PubMed
-
- Harris KA, Holly RG. Physiological response to circuit weight training in borderline hypertensive subjects. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1987;19:246–52. - PubMed
-
- Haslam DRS, McCartney N, McKelvie RS, MacDougall JD. Direct measurements of arterial blood pressure during formal weightlifting in cardiac patients. J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 1988;8:213–25.

