Effect of combined hormonal and insulin therapy on the steroid hormone receptors and growth factors signalling in diabetic mice prostate
- PMID: 21039986
- PMCID: PMC3010553
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00739.x
Effect of combined hormonal and insulin therapy on the steroid hormone receptors and growth factors signalling in diabetic mice prostate
Abstract
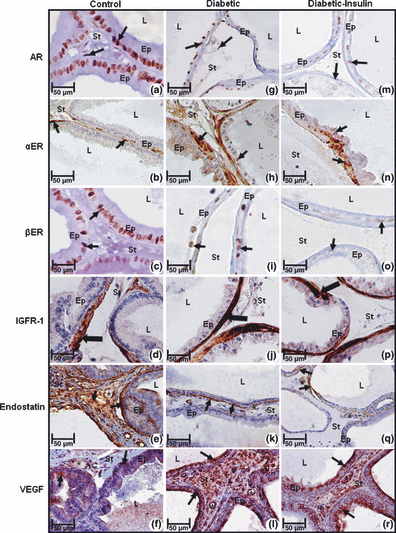
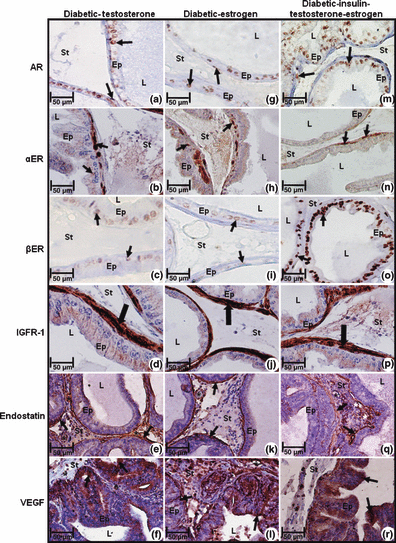
Diabetes causes harmful effects on prostatic morphology and function. However, there still are doubts about the occurrence of various diseases in the prostate, as well as abnormal angiogenesis in relation to diabetes. Thus, the aim of this study was to correlate and quantify the level of the steroid hormone receptors and the angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in non-obese diabetic mice (Nod) after combined hormonal and insulin therapy. Sixty mice were divided into six groups after 20 days of diabetes: the control group received 0.9% NaCl, as did the diabetic group. The diabetic-insulin group received insulin, the diabetic-testosterone group received testosterone cypionate, the diabetic-oestrogen group received 17β-oestradiol, and the diabetic-insulin-testosterone-oestrogen group received insulin, testosterone and oestrogen simultaneously. After 20 days, the ventral lobe was processed for immunocytochemical and hormonal analyses. The results showed that the lowest serum testosterone and androgen receptor levels were found in the diabetic group and the highest testosterone and androgen receptor levels in the diabetic-insulin-testosterone-oestrogen group. The serum oestrogen level and its receptor showed changes opposite to those of testosterone and its receptor. The endostatin reactivity was mainly decreased in diabetic mice. The greatest IGFR-1 and VEGF reactivities occurred in diabetic mice. Thus, diabetes led to the prostatic hormonal imbalance, affecting molecular dynamics and angiogenesis in this organ. Combined insulin and steroid hormone therapy partially restored the hormonal and angiogenic imbalance caused by diabetes.
© 2010 The Authors. International Journal of Experimental Pathology © 2010 International Journal of Experimental Pathology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrastructural and proliferative features of the ventral lobe of the prostate in non-obese diabetic mice (NOD) following androgen and estrogen replacement associated to insulin therapy.Tissue Cell. 2009 Apr;41(2):119-32. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2008.09.001. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Tissue Cell. 2009. PMID: 19019401
-
Senescence and steroid hormone receptor reactivities in accessory sex glands of elderly rats (Sprague-Dawley) following exogenous hormonal therapy.Tissue Cell. 2012 Aug;44(4):227-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Tissue Cell. 2012. PMID: 22541803
-
Angiogenic and tissue remodeling factors in the prostate of elderly rats submitted to hormonal replacement.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013 Nov;296(11):1758-67. doi: 10.1002/ar.22786. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2013. PMID: 24106075
-
Hormonal therapy in the senescence: Prostatic microenvironment structure and adhesion molecules.Micron. 2011 Aug;42(6):642-55. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Micron. 2011. PMID: 21489806
-
Current applications of PET imaging of sex hormone receptors with a fluorinated analogue of estradiol or of testosterone.Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Mar;59(1):4-17. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25693420 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity and metabolic dysfunction severely influence prostate cell function: role of insulin and IGF1.J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Sep;21(9):1893-1904. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13109. Epub 2017 Feb 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28244645 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic rapamycin treatment causes diabetes in male mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014 Aug 15;307(4):R434-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00123.2014. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24965794 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Melatonin on the Proliferative and Apoptotic Responses of the Prostate under Normal and Hyperglycemic Conditions.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:538529. doi: 10.1155/2015/538529. Epub 2015 Jul 30. J Diabetes Res. 2015. PMID: 26295055 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into the use of rhubarb in diabetic kidney disease treatment using network pharmacology.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jan 7;101(1):e28465. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028465. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35029893 Free PMC article.
-
Physical resistance training-induced changes in lipids metabolism pathways and apoptosis in prostate.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Jan 29;19(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-1195-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 31996229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdollahi A, Lipson KE, Sckell A, et al. Combined therapy with direct and indirect angiogenesis inhibition results in enhanced antiangiogenic and antitumor effects. Cancer Res. 2003;63:8890–8898. - PubMed
-
- Aiello LP, Wong JS. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic vascular complications. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2000;77:113–119. - PubMed
-
- Anderson LC. Effects of alloxan diabetes and insulin in vivo on rat parotid gland. Am. J. Physiol. 1983;245:431–437. - PubMed
-
- Asai K, Kanazawa H, Otani K, Shiraishi S, Hirata K, Yoshikawa J. Imbalance between vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin levels in induced sputum from asthmatic subjects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002;110:571–575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

