Identification of tyrosine-nitrated proteins in HT22 hippocampal cells during glutamate-induced oxidative stress
- PMID: 21039997
- PMCID: PMC6496341
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2010.00708.x
Identification of tyrosine-nitrated proteins in HT22 hippocampal cells during glutamate-induced oxidative stress
Abstract
Objectives: Nitration of tyrosine residues in protein is a post-translational modification, which occurs under oxidative stress, and is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. To understand the role of nitrated proteins in oxidative stress-induced cell death, we identified nitrated proteins and checked correlation of their nitration in glutamate-induced HT22 cell death.
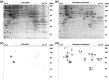
Materials and methods: Nitrated proteins were detected by western blotting using an anti-nitrotyrosine antibody, extracted from matching reference 2-dimensional electrophoresis gels, and identified with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Results: Glutamate treatment induced apoptosis in HT22 cells, while reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibitor or neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) inhibitor blocked glutamate-induced HT22 cell death. Nitration levels of 13 proteins were increased after glutamate stimulation; six of them were involved in regulation of energy production and two were related to apoptosis. The other nitrated proteins were associated with calcium signal modulation, ER dysfunction, or were of unknown function.
Conclusions: The 13 tyrosine-nitrated proteins were detected in these glutamate-treated HT22 cells. Results demonstrated that cell death, ROS accumulation and nNOS expression were related to nitration of protein tyrosine in the glutamate-stimulated cells.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mapping sites of tyrosine nitration by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry.Methods Enzymol. 2005;396:266-75. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(05)96023-0. Methods Enzymol. 2005. PMID: 16291238
-
Tyrosine-Nitrated Proteins: Proteomic and Bioanalytical Aspects.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017 Mar 1;26(7):313-328. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6787. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2017. PMID: 27324931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kaempferol attenuates the glutamate-induced oxidative stress in mouse-derived hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells.Food Funct. 2014 Jul 25;5(7):1395-402. doi: 10.1039/c4fo00068d. Food Funct. 2014. PMID: 24770605
-
The neuroprotective effects of cordycepin inhibit glutamate-induced oxidative and ER stress-associated apoptosis in hippocampal HT22 cells.Neurotoxicology. 2014 Mar;41:102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.01.005. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Neurotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 24486958
-
Detecting nitrated proteins by proteomic technologies.Methods Enzymol. 2008;440:17-31. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)00802-6. Methods Enzymol. 2008. PMID: 18423209 Review.
Cited by
-
Pretreatment with 2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-β-D-pyranoside attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in vitro and in vivo.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e100126. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100126. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24991917 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation renders susceptibility to excitotoxicity in HT22 neurons.Neural Regen Res. 2013 May 15;8(14):1297-306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2013.14.006. Neural Regen Res. 2013. PMID: 25206424 Free PMC article.
-
Method for detection of hydrogen peroxide in HT22 cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 30;7:45673. doi: 10.1038/srep45673. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28358356 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin abates hypoxia-induced oxidative stress based-ER stress-mediated cell death in mouse hippocampal cells (HT22) by controlling Prdx6 and NF-κB regulation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013 Apr 1;304(7):C636-55. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00345.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23364261 Free PMC article.
-
Cis-[Cr(C2O4)(pm)(OH2)2]+ coordination ion as a specific sensing ion for H2O2 detection in HT22 cells.Molecules. 2014 Jun 23;19(6):8533-43. doi: 10.3390/molecules19068533. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24959680 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mattson MP (2000) Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 120–129. - PubMed
-
- Davies KJ, Delsignore ME, Lin SW (1987) Protein damage and degradation by oxygen radicals. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 9902–9907. - PubMed
-
- Bowler RP, Crapo JD (2002) Oxidative stress in allergic respiratory diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 110, 349–356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

