5-Hydroxytryptophan during critical postnatal period improves cognitive performances and promotes dendritic spine maturation in genetic mouse model of phenylketonuria
- PMID: 21040618
- PMCID: PMC3110346
- DOI: 10.1017/S1461145710001288
5-Hydroxytryptophan during critical postnatal period improves cognitive performances and promotes dendritic spine maturation in genetic mouse model of phenylketonuria
Abstract
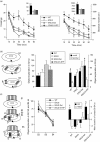
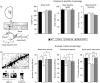
Although phenylketonuria (PKU) is the most common genetic cause of mental retardation, the cellular mechanisms underlying impaired brain function are still unclear. Using PAHenu2 mice (ENU2), the genetic mouse model of PKU, we previously demonstrated that high phenylalanine levels interfere with brain tryptophan hydroxylase activity by reducing the availability of serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), crucial for maturation of neuronal connectivity in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), around the third postnatal week, a critical period for cortical maturation. 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), the product of tryptophan hydroxylation, is known to be a better treatment to increase brain 5-HT levels. In this study we investigated the role of 5-HT during the early postnatal period in cognitive disturbances and in cortical dendritic alterations of PKU subjects by restoring temporarily (postnatal days 14-21) physiological brain levels of 5-HT in ENU2 through 5-HTP treatment. In adult ENU2 mice early 5-HTP treatment reverses cognitive deficits in spatial and object recognition tests accompanied by an increase in spine maturation of pyramidal neurons in layer V of the prelimbic/infralimbic area of the PFC, although locomotor deficits are not recovered by treatment. Taken together, our results support the hypothesis that mental retardation in PKU depends on reduced availability of brain 5-HT during critical developmental periods that interferes with cortical maturation and point to 5-HTP supplementation as a highly promising additional tool to heal PKU patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Hydroxytryptophan rescues serotonin response to stress in prefrontal cortex of hyperphenylalaninaemic mice.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Sep;12(8):1067-79. doi: 10.1017/S1461145709990381. Epub 2009 Aug 10. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19664307
-
Reduced availability of brain amines during critical phases of postnatal development in a genetic mouse model of cognitive delay.Brain Res. 2008 Jun 27;1217:232-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.04.006. Epub 2008 Apr 16. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18502400
-
Blood phenylalanine reduction corrects CNS dopamine and serotonin deficiencies and partially improves behavioral performance in adult phenylketonuric mice.Mol Genet Metab. 2018 Jan;123(1):6-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 19. Mol Genet Metab. 2018. PMID: 29331172 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the importance of dopamine for prefrontal cortex functions early in life.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Oct 29;351(1346):1483-93; discussion 1494. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0134. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8941960 Review.
-
Can untreated PKU patients escape from intellectual disability? A systematic review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018 Aug 29;13(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s13023-018-0890-7. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2018. PMID: 30157945 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Phenylalanine-Treated Human Neuronal Model: Spotlight on Neurite Impairment and Synaptic Connectivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 18;25(18):10019. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810019. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337507 Free PMC article.
-
Role of prefrontal 5-HT in the strain-dependent variation in sign-tracking behavior of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016 Apr;233(7):1157-69. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4192-7. Epub 2016 Jan 4. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2016. PMID: 26728892
-
Cognitive Functioning in Adults with Phenylketonuria in a Cohort of Spanish Patients.Behav Neurol. 2023 Feb 8;2023:9681740. doi: 10.1155/2023/9681740. eCollection 2023. Behav Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36815863 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a co-treatment with pyruvate and creatine on dendritic spines in rat hippocampus and posterodorsal medial amygdala in a phenylketonuria animal model.Metab Brain Dis. 2013 Sep;28(3):509-17. doi: 10.1007/s11011-013-9389-z. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Metab Brain Dis. 2013. PMID: 23430365
-
Unbalance between Excitation and Inhibition in Phenylketonuria, a Genetic Metabolic Disease Associated with Autism.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 29;18(5):941. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050941. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28468253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akirav I, Maroun M. Ventromedial prefrontal cortex is obligatory for consolidation and reconsolidation of object recognition memory. Cerebral Cortex. 2006;16:1759–1765. - PubMed
-
- Bauman ML, Kemper TL. Morphologic and histoanatomic observations of the brain in untreated phenylketonuria. Acta Neuropathologica. 1982;58:55–63. - PubMed
-
- Bennett-Clarke CA, Lane RD, Rhoades RW. Fenfluramine depletes serotonin from the developing cortex and alters thalamocortical organization. Brain Research. 1995;702:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Burlina A, Blau N. Effect of (BH)4 supplementation on phenylalanine tolerance. Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease. 2009;32:40–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

