Sporadic reappearance of minute amounts of hepatitis C virus RNA after successful therapy stimulates cellular immune responses
- PMID: 21040725
- PMCID: PMC3399733
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.10.048
Sporadic reappearance of minute amounts of hepatitis C virus RNA after successful therapy stimulates cellular immune responses
Abstract
Background & aims: Several studies have reported hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA sequences in the circulation after treatment-induced or spontaneous recovery. We investigated whether the HCV RNA represents persistence of HCV infection or reinfection.
Methods: We studied 117 patients who recovered from HCV infection (98 following therapy and 19 spontaneously). A reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay was used to detect the 5'-untranslated region of HCV. T-cell responses were studied by enzyme-linked immunospot for interferon-γ.
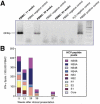
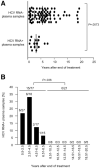
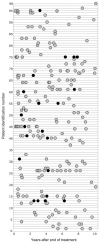
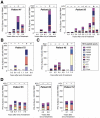
Results: Plasma samples from 15% of treatment-recovered patients and no spontaneously recovered patient tested positive for HCV RNA. Lymphocytes from 3 patients who responded to therapy and 1 who recovered spontaneously tested positive. The frequency of HCV RNA detection in plasma correlated inversely with the time after the end of treatment. Post-treatment HCV 5'-untranslated region sequences matched pretreatment sequences in 85% of cases. T-cell responses were significantly greater at time points with detectable trace amounts of HCV RNA than at time points without detectable HCV RNA (P = .035) and were primarily against nonstructural HCV antigens. The immune hierarchy was preserved over 5 years in patients whose post-treatment HCV RNA sequences matched pretreatment sequences, indicating HCV RNA persistence. An altered immune hierarchy with dominant immune responses, shifting from nonstructural to structural antigens, was observed in a single patient whose post-treatment HCV genotype differed from that of the pretreatment genotype, indicating HCV reinfection.
Conclusions: Trace amounts of HCV RNA of pretreatment sequence persisted and reappeared sporadically in the circulation within 8 years after recovery from hepatitis C but not thereafter, indicating that patients are cured of HCV infection. Reappearance of HCV RNA induced HCV-specific T-cell responses.
Copyright © 2011 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequential changes of hepatitis C virus antibody profiles during treatment of chronic hepatitis C of genotype 1b: pretreatment antibody response to E2/NS1 correlated sustained response.Infection. 2004 Jun;32(3):153-6. doi: 10.1007/s15010-004-3133-x. Infection. 2004. PMID: 15188075
-
High rate of spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C virus genotype 3 infection.J Med Virol. 2004 Jul;73(3):387-91. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20103. J Med Virol. 2004. PMID: 15170633
-
Long-term follow-up of successful hepatitis C virus therapy: waning immune responses and disappearance of liver disease are consistent with cure.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Mar;41(6):532-43. doi: 10.1111/apt.13096. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25627143
-
Strong hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific cell-mediated immune responses in the absence of viremia or antibodies among uninfected siblings of HCV chronically infected children.J Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 15;203(6):854-61. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq123. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21257736 Free PMC article.
-
Could a loss of memory T cells limit responses to hepatitis C virus (HCV) antigens in blood leucocytes from patients chronically infected with HCV before and during pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy?Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;161(1):118-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04141.x. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20408862 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Regulatory polymorphism of CXCL10 rs1439490 in seronegative occult hepatitis C virus infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 May 28;24(20):2191-2202. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i20.2191. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29853737 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sequence analysis of hepatitis C virus from patients with relapse after a sustained virological response: relapse or reinfection?J Infect Dis. 2014 Jan 1;209(1):38-45. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit541. Epub 2013 Oct 14. J Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24127561 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of hepatitis C viral RNA persistence in HIV-infected patients with long-term sustained virological response by droplet digital PCR.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 29;9(1):12507. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48966-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31467339 Free PMC article.
-
According to Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Infection Stage, Interleukin-7 Plus 4-1BB Triggering Alone or Combined with PD-1 Blockade Increases TRAF1low HCV-Specific CD8+ Cell Reactivity.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e01443-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01443-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29093082 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous clearance of viral infections by mesoscopic fluctuations.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038549. Epub 2012 Jun 5. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22693646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feld JJ, Hoofnagle JH. Mechanism of action of interferon and ribavirin in treatment of hepatitis C. Nature. 2005;436:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Radkowski M, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Jablonska J, et al. Persistence of hepatitis C virus in patients successfully treated for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2005;41:106–114. - PubMed
-
- Castillo I, Rodriguez-Inigo E, Lopez-Alcorocho JM, et al. Hepatitis C virus replicates in the liver of patients who have a sustained response to antiviral treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;43:1277–1283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

