Single-cell optogenetic excitation drives homeostatic synaptic depression
- PMID: 21040851
- PMCID: PMC3111089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.020
Single-cell optogenetic excitation drives homeostatic synaptic depression
Abstract
Homeostatic processes have been proposed to explain the discrepancy between the dynamics of synaptic plasticity and the stability of brain function. Forms of synaptic plasticity such as long-term potentiation alter synaptic activity in a synapse- and cell-specific fashion. Although network-wide excitation triggers compensatory homeostatic changes, it is unknown whether neurons initiate homeostatic synaptic changes in response to cell-autonomous increases in excitation. Here we employ optogenetic tools to cell-autonomously excite CA1 pyramidal neurons and find that a compensatory postsynaptic depression of both AMPAR and NMDAR function results. Elevated calcium influx through L-type calcium channels leads to activation of a pathway involving CaM kinase kinase and CaM kinase 4 that induces synaptic depression of AMPAR and NMDAR responses. The synaptic depression of AMPARs but not of NMDARs requires protein synthesis and the GluA2 AMPAR subunit, indicating that downstream of CaM kinase activation divergent pathways regulate homeostatic AMPAR and NMDAR depression.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
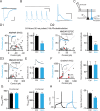
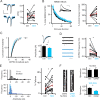
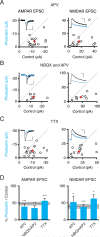
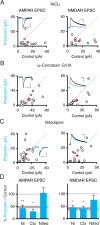
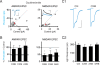
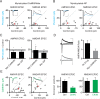
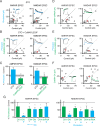
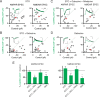
Comment in
-
Homeostatic plasticity: single hippocampal neurons see the light.Neuron. 2010 Nov 4;68(3):326-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.10.025. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21040836
-
Plasticity: Don't get too excited!Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 Jan;12(1):6. doi: 10.1038/nrn2966. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21218573 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Control of Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity by AKAP-Anchored Kinase and Phosphatase Regulation of Ca2+-Permeable AMPA Receptors.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 14;38(11):2863-2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2362-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29440558 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Excitation/Inhibition Balance in a Hippocampal Circuit by Calcium Sensor Protein Regulation of Presynaptic Calcium Channels.J Neurosci. 2018 May 2;38(18):4430-4440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0022-18.2018. Epub 2018 Apr 13. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29654190 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-calmodulin signalling pathway up-regulates glutamatergic synaptic function in non-pyramidal, fast spiking rat hippocampal CA1 neurons.J Physiol. 2001 Jun 1;533(Pt 2):407-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0407a.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11389201 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
The AMPA Receptor Code of Synaptic Plasticity.Neuron. 2018 Oct 24;100(2):314-329. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.018. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30359599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Delayed in vitro development of Up states but normal network plasticity in Fragile X circuits.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Sep;42(6):2312-21. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13010. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26138886 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged esophageal acid exposures induce synaptic downscaling of cortical membrane AMPA receptor subunits in rats.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Sep;28(9):1356-69. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12834. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 27271201 Free PMC article.
-
CaMKIV Signaling Is Not Essential for the Maintenance of Intrinsic or Synaptic Properties in Mouse Visual Cortex.eNeuro. 2021 Jul 6;8(4):ENEURO.0135-21.2021. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0135-21.2021. Print 2021 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2021. PMID: 34001638 Free PMC article.
-
Topological Regulation of Synaptic AMPA Receptor Expression by the RNA-Binding Protein CPEB3.Cell Rep. 2016 Sep 27;17(1):86-103. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.094. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27681423 Free PMC article.
-
AMPA receptor trafficking in homeostatic synaptic plasticity: functional molecules and signaling cascades.Neural Plast. 2012;2012:825364. doi: 10.1155/2012/825364. Epub 2012 May 13. Neural Plast. 2012. PMID: 22655210 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

