Increased adipose tissue lipolysis after a 2-week high-fat diet in sedentary overweight/obese men
- PMID: 21040937
- PMCID: PMC3868457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2010.09.007
Increased adipose tissue lipolysis after a 2-week high-fat diet in sedentary overweight/obese men
Abstract
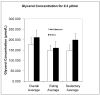
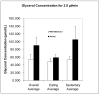
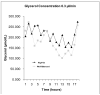
The purpose of this study was to determine if a high-fat diet would result in a higher lipolytic rate in subcutaneous adipose tissue than a lower-fat diet in sedentary nonlean men. Six participants (healthy males; 18-40 years old; body mass index, 25-37 kg/m(2)) underwent 2 weeks on a high-fat or well-balanced diet of similar energy content (approximately 6695 kJ) in randomized order with a 10-day washout period between diets. Subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue lipolysis was determined over the course of a day using microdialysis after both 2-week diet sessions. Average interstitial glycerol concentrations (index of lipolysis) as determined using microdialysis were higher after the high-fat diet (210.8 ± 27.9 μmol/L) than after a well-balanced diet (175.6 ± 23.3 μmol/L; P = .026). There was no difference in adipose tissue microvascular blood flow as determined using the microdialysis ethanol technique. These results demonstrate that healthy nonlean men who diet on the high-fat plan have a higher lipolytic rate in subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue than when they diet on a well-balanced diet plan. This higher rate of lipolysis may result in a higher rate of fat mass loss on the high-fat diet; however, it remains to be determined if this higher lipolytic rate in men on the high-fat diet results in a more rapid net loss of triglyceride from the abdominal adipose depots, or if the higher lipolytic rate is counteracted by an increased rate of lipid storage.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- American College of Sports Medicine . ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. 7th Edition Philadelphia, PA: 2005. p. 366. - PubMed
-
- Baker B. Weight loss and diet plans. Am J Nurs. 2006;106(6):52–59. quiz 60. - PubMed
-
- Burke V, Beilin L, Cutt H, Mansour J, Williams A, Mori T. A lifestyle program for treated hypertensives improved health-related behaviors and cardiovascular risk factors, a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Epidemiol. 2007;60(2):133–141. - PubMed
-
- Fellander G, Linde B, Bolinder J. Evaluation of the microdialysis ethanol technique for monitoring of subcutaneous adipose tissue blood flow in humans. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996 Mar;20(3):220–6. - PubMed
-
- Gesta S, Hejnova J, Berlan M, Daviaud D, Crampes F, Stich V, Valet P, Saulnier-Blache J. In vitro and in vivo impairment of alpha2-adrenergic receptor-dependent antilipolysis by fatty acids in human adipose tissue. Horm Metab Res. 2001;33(12):701–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

