In vivo tissue responses to thermal-responsive shape memory polymer nanocomposites
- PMID: 21040968
- PMCID: PMC2992594
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.012
In vivo tissue responses to thermal-responsive shape memory polymer nanocomposites
Abstract
To explore the safe use of thermal-responsive shape memory polymers (SMPs) as minimally invasive tissue scaffolds, we recently developed a class of biodegradable POSS-SMP nanocomposites exhibiting stable temporary shape fixing and facile shape recovery within a narrow window of physiological temperatures. The materials were covalently crosslinked from star-branched building blocks consisting a bioinert polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS) core and 8 degradable poly(D,L-lactide) (PLA) arms. Here we examine the degradation profiles and immunogenicity of POSS-SMPs as a function of the PLA arm lengths using a rat subcutaneous implantation model. We show that POSS-SMPs elicited a mild foreign body type immune response upon implantation. The degradation rates of POSS-SMPs, both in vitro and in vivo, inversely correlated with the length of the PLA chains within the crosslinked amorphous network. Upon in vivo degradation of POSS-SMPs, a second acute inflammatory response was elicited locally, and the inflammation was able to resolve over time without medical interventions. One year after the implantation of POSS-SMPs, no pathologic abnormalities were detected from the vital/scavenger organs examined. These minimally immunogenic and biodegradable SMPs are promising candidates for scaffold-assisted tissue repair where both facile surgical delivery and controlled degradation of the scaffold are desired for achieving optimal short-term and long-term clinical outcomes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



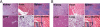
References
-
- Karp JM, Langer R. Development and therapeutic applications of advanced biomaterials. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2007;18:454–9. - PubMed
-
- Sokolowski W, Metcalfe A, Hayashi S, Yahia L, Raymond J. Medical applications of shape memory polymers. Biomed Mater. 2007;2:S23–7. - PubMed
-
- Pearce AI, Richards RG, Milz S, Schneider E, Pearce SG. Animal models for implant biomaterial research in bone: A review. Eur Cells Mater. 2007;13:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Williams DF. On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2941–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

