Developmental dynamics of piriform cortex
- PMID: 21041199
- PMCID: PMC3140179
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq199
Developmental dynamics of piriform cortex
Abstract
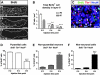
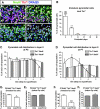
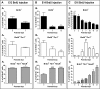
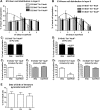
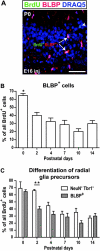
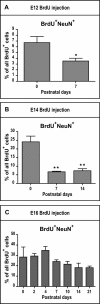
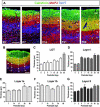
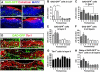
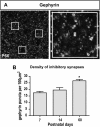
The piriform cortex (PCX) is a trilaminar paleocortex that is of interest for its role in odor coding and as a model for studying general principles of cortical sensory processing. While the structure of the mature PCX has been well characterized, its development is poorly understood. Notably, the kinetics as well as the cellular and morphological basis of the postnatal events that shape the PCX remain unknown. We followed the cellular fates of early- versus late-born cells in layer II of the anterior PCX, with a focus on the molecular maturation of pyramidal cells and the kinetics of their differentiation. We showed that: 1) early-born pyramidal cells differentiate more rapidly than late-born cells and 2) the position of pyramidal cells within the thickness of layer II determines the kinetics of their molecular maturation. We then examined the postnatal development of cortical lamination and showed that the establishment of inhibitory networks in the PCX proceeds through an increase in the density of inhibitory synapses despite a decrease in the number of interneurons. Together, our results provide a more comprehensive view of the postnatal development of the anterior PCX and reveal both similarities and differences in the development of this paleocortex versus the neocortex.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JL. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997;278:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Angevine JB, Jr., Sidman RL. Autoradiographic study of cell migration during histogenesis of cerebral cortex in the mouse. Nature. 1961;192:766–768. - PubMed
-
- Anthony TE, Klein C, Fishell G, Heintz N. Radial glia serve as neuronal progenitors in all regions of the central nervous system. Neuron. 2004;41:881–890. - PubMed
-
- Bayer SA. Neurogenesis in the rat primary olfactory cortex. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1986;4:251–271. - PubMed

