Cytoplasmic ASPP1 inhibits apoptosis through the control of YAP
- PMID: 21041411
- PMCID: PMC2964753
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1954310
Cytoplasmic ASPP1 inhibits apoptosis through the control of YAP
Abstract
The ASPP (apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53) family of proteins can function in the nucleus to modulate the transcriptional activity of p53, with ASPP1 and ASPP2 contributing to the expression of apoptotic target genes. In this study, we describe a new function for cytoplasmic ASPP1 in controlling YAP (Yes-associated protein)/TAZ. ASPP1 can inhibit the interaction of YAP with LATS1 (large tumor suppressor 1), a kinase that phosphorylates YAP/TAZ and promotes cytoplasmic sequestration and protein degradation. This function of ASPP1 therefore enhances nuclear accumulation of YAP/TAZ and YAP/TAZ-dependent transcriptional regulation. The consequence of YAP/TAZ activation by ASPP1 is to inhibit apoptosis, in part through the down-regulation of Bim expression, leading to resistance to anoikis and enhanced cell migration. These results reveal a potential oncogenic role for cytoplasmic ASPP1, in contrast to the tumor-suppressive activity described previously for nuclear ASPP1.
Figures
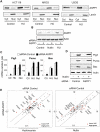
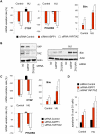
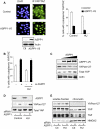
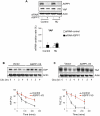



Comment in
-
YAP tips the balance.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Dec;10(12):811. doi: 10.1038/nrc2973. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21155175 No abstract available.
References
-
- Agirre X, Roman-Gomez J, Jimenez-Velasco A, Garate L, Montiel-Duarte C, Navarro G, Vazquez I, Zalacain M, Calasanz MJ, Heiniger A, et al. 2006. ASPP1, a common activator of TP53, is inactivated by aberrant methylation of its promoter in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncogene 25: 1862–1870 - PubMed
-
- Bergamaschi D, Samuels-Lev Y, O'Neil NJ, Trigiante G, Crook T, Hseih JK, O'Conner DJ, Zhong S, Compargue I, Tomlinson ML, et al. 2003. iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worms to humans. Nat Genet 33: 162–167 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
