The Cdc42-selective GAP rich regulates postsynaptic development and retrograde BMP transsynaptic signaling
- PMID: 21041451
- PMCID: PMC3003324
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201007086
The Cdc42-selective GAP rich regulates postsynaptic development and retrograde BMP transsynaptic signaling
Abstract
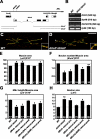
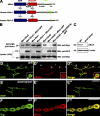
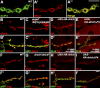
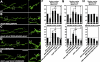
Retrograde bone morphogenetic protein signaling mediated by the Glass bottom boat (Gbb) ligand modulates structural and functional synaptogenesis at the Drosophila melanogaster neuromuscular junction. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating postsynaptic Gbb release are poorly understood. In this study, we show that Drosophila Rich (dRich), a conserved Cdc42-selective guanosine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP), inhibits the Cdc42-Wsp pathway to stimulate postsynaptic Gbb release. Loss of dRich causes synaptic undergrowth and strongly impairs neurotransmitter release. These presynaptic defects are rescued by targeted postsynaptic expression of wild-type dRich but not a GAP-deficient mutant. dRich inhibits the postsynaptic localization of the Cdc42 effector Wsp (Drosophila orthologue of mammalian Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASp), and manifestation of synaptogenesis defects in drich mutants requires Wsp signaling. In addition, dRich regulates postsynaptic organization independently of Cdc42. Importantly, dRich increases Gbb release and elevates presynaptic phosphorylated Mad levels. We propose that dRich coordinates the Gbb-dependent modulation of synaptic growth and function with postsynaptic development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
dCIP4 (Drosophila Cdc42-interacting protein 4) restrains synaptic growth by inhibiting the secretion of the retrograde Glass bottom boat signal.J Neurosci. 2010 Jun 16;30(24):8138-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0256-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20554864 Free PMC article.
-
Crimpy enables discrimination of presynaptic and postsynaptic pools of a BMP at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Dev Cell. 2014 Dec 8;31(5):586-98. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 25453556 Free PMC article.
-
Crimpy inhibits the BMP homolog Gbb in motoneurons to enable proper growth control at the Drosophila neuromuscular junction.Development. 2011 Aug;138(15):3273-86. doi: 10.1242/dev.066142. Development. 2011. PMID: 21750037 Free PMC article.
-
Morphogens and synaptogenesis in Drosophila.J Neurobiol. 2005 Sep 15;64(4):417-34. doi: 10.1002/neu.20165. J Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16041756 Review.
-
Orchestrating development and function: retrograde BMP signaling in the Drosophila nervous system.Trends Neurosci. 2004 Mar;27(3):143-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2004.01.004. Trends Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15036879 Review.
Cited by
-
N-glycosylation requirements in neuromuscular synaptogenesis.Development. 2013 Dec;140(24):4970-81. doi: 10.1242/dev.099192. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Development. 2013. PMID: 24227656 Free PMC article.
-
Tricornered Kinase Regulates Synapse Development by Regulating the Levels of Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 22;10(9):e0138188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138188. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26393506 Free PMC article.
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein regulates trans-synaptic signaling in Drosophila.Dis Model Mech. 2013 Nov;6(6):1400-13. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012229. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Dis Model Mech. 2013. PMID: 24046358 Free PMC article.
-
Two protein N-acetylgalactosaminyl transferases regulate synaptic plasticity by activity-dependent regulation of integrin signaling.J Neurosci. 2014 Sep 24;34(39):13047-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1484-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25253852 Free PMC article.
-
The NDR family of kinases: essential regulators of aging.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 May 13;17:1371086. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1371086. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38803357 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brand A.H., Perrimon N. 1993. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 118:401–415 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

