A BAFF-R mutation associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma alters TRAF recruitment and reveals new insights into BAFF-R signaling
- PMID: 21041452
- PMCID: PMC2989778
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20100857
A BAFF-R mutation associated with non-Hodgkin lymphoma alters TRAF recruitment and reveals new insights into BAFF-R signaling
Abstract
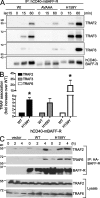
The cytokine B cell activating factor (BAFF) and its receptor, BAFF receptor (BAFF-R), modulate signaling cascades critical for B cell development and survival. We identified a novel mutation in TNFRSF13C, the gene encoding human BAFF-R, that is present in both tumor and germline tissue from a subset of patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This mutation encodes a His159Tyr substitution in the cytoplasmic tail of BAFF-R adjacent to the TRAF3 binding motif. Signaling through this mutant BAFF-R results in increased NF-κB1 and NF-κB2 activity and increased immunoglobulin production compared with the wild-type (WT) BAFF-R. This correlates with increased TRAF2, TRAF3, and TRAF6 recruitment to His159Tyr BAFF-R. In addition, we document a requirement for TRAF6 in WT BAFF-R signaling. Together, these data identify a novel lymphoma-associated mutation in human BAFF-R that results in NF-κB activation and reveals TRAF6 as a necessary component of normal BAFF-R signaling.
Figures


References
-
- Beghini A., Tibiletti M.G., Roversi G., Chiaravalli A.M., Serio G., Capella C., Larizza L. 2001. Germline mutation in the juxtamembrane domain of the kit gene in a family with gastrointestinal stromal tumors and urticaria pigmentosa. Cancer. 92:657–662 10.1002/1097-0142(20010801)92:3<657::AID-CNCR1367>3.0.CO;2-D - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

