Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study
- PMID: 21041710
- PMCID: PMC3058272
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.30.1655
Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study
Abstract
Purpose: This European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial assesses whether adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) increases the duration of functional independence after surgery or radiosurgery of brain metastases.
Patients and methods: Patients with one to three brain metastases of solid tumors (small-cell lung cancer excluded) with stable systemic disease or asymptomatic primary tumors and WHO performance status (PS) of 0 to 2 were treated with complete surgery or radiosurgery and randomly assigned to adjuvant WBRT (30 Gy in 10 fractions) or observation (OBS). The primary end point was time to WHO PS deterioration to more than 2.
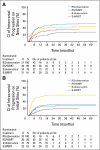
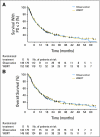
Results: Of 359 patients, 199 underwent radiosurgery, and 160 underwent surgery. In the radiosurgery group, 100 patients were allocated to OBS, and 99 were allocated to WBRT. After surgery, 79 patients were allocated to OBS, and 81 were allocated to adjuvant WBRT. The median time to WHO PS more than 2 was 10.0 months (95% CI, 8.1 to 11.7 months) after OBS and 9.5 months (95% CI, 7.8 to 11.9 months) after WBRT (P = .71). Overall survival was similar in the WBRT and OBS arms (median, 10.9 v 10.7 months, respectively; P = .89). WBRT reduced the 2-year relapse rate both at initial sites (surgery: 59% to 27%, P < .001; radiosurgery: 31% to 19%, P = .040) and at new sites (surgery: 42% to 23%, P = .008; radiosurgery: 48% to 33%, P = .023). Salvage therapies were used more frequently after OBS than after WBRT. Intracranial progression caused death in 78 (44%) of 179 patients in the OBS arm and in 50 (28%) of 180 patients in the WBRT arm.
Conclusion: After radiosurgery or surgery of a limited number of brain metastases, adjuvant WBRT reduces intracranial relapses and neurologic deaths but fails to improve the duration of functional independence and overall survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
The dandelion effect: treat the whole lawn or weed selectively?J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jan 10;29(2):121-4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.3294. Epub 2010 Dec 6. J Clin Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21135269 No abstract available.
-
Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study.Curr Oncol Rep. 2011 Aug;13(4):255-8. doi: 10.1007/s11912-011-0180-1. Curr Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21584645 No abstract available.
References
-
- Soffietti R, Rudà R, Trevisan E. Brain metastases: Current management and new developments. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20:676–684. - PubMed
-
- Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:494–500. - PubMed
-
- Noordijk EM, Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, et al. The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994;29:711–717. - PubMed
-
- Borgelt B, Gelber R, Kramer S. The palliation of brain metastases: Final results of the first two studies by the RTOG. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980;6:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Sturm V, Kober B, Höver KH, et al. Stereotactic percutaneous single dose irradiation of brain metastases with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1987;13:279–282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

