Expression of ARC (apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain), an antiapoptotic protein, is strongly prognostic in AML
- PMID: 21041716
- PMCID: PMC3035072
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-280503
Expression of ARC (apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain), an antiapoptotic protein, is strongly prognostic in AML
Abstract
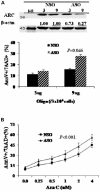
Regulators of apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have been extensively studied and are considered excellent therapeutic targets. Apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain (ARC), an antiapoptotic protein originally found to be involved in apoptosis of cardiac cells, was recently demonstrated to be overexpressed in several solid tumors. To assess its importance in AML, we profiled ARC expression in 511 newly diagnosed AML patients using a validated robust reverse-phase protein array and correlated ARC levels with clinical outcomes. ARC was variably expressed in samples from patients with AML. ARC level was not associated with cytogenetic groups or with FLT-3 mutation status. However, patients with low or medium ARC protein levels had significantly better outcomes than those with high ARC levels: longer overall survival (median, 53.9 or 61.6 vs 38.9 weeks, P = .0015) and longer remission duration (median, 97.6 or 44.7 vs 31.1 weeks, P = .0007). Multivariate analysis indicated that ARC was a statistically significant independent predictor of survival in AML (P = .00013). Inhibition of ARC promoted apoptosis and sensitized cytosine arabinoside-induced apoptosis in OCI-AML3 cells. These results suggest that ARC expression levels are highly prognostic in AML and that ARC is a potential therapeutic target in AML.
Figures





References
-
- Green DR, Evan GI. A matter of life and death. Cancer Cell. 2002;1(1):19–30. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Ge X, Liu X. The cardioprotective effect of postconditioning is mediated by ARC through inhibiting mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis. 2009;14(2):164–172. - PubMed
-
- Li YZ, Liu XH, Zhu XM, Cai LR. ARC contributes to the inhibitory effect of preconditioning on cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis. 2007;12(9):1589–1595. - PubMed
-
- Hong YM, Jo DG, Lee JY, et al. Down-regulation of ARC contributes to vulnerability of hippocampal neurons to ischemia/hypoxia. FEBS Lett. 2003;543(1):170–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

