Toxicologic effects of gold nanoparticles in vivo by different administration routes
- PMID: 21042423
- PMCID: PMC2962273
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S8428
Toxicologic effects of gold nanoparticles in vivo by different administration routes
Abstract
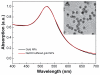
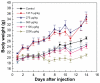
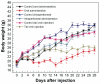
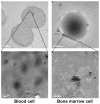
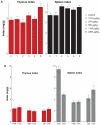
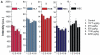
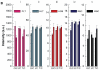
Gold nanoparticles have potential applications in biomedicine, but one of the important concerns is about their safety. Most toxicology data are derived from in vitro studies and may not reflect in vivo responses. Here, an animal toxicity study of 13.5 nm gold nanoparticles in mice is presented. Animal survival, weight, hematology, morphology, and organ index are characterized at different concentrations (137.5-2200 μg/kg) over 14-28 days. The results show that low concentrations of gold nanoparticles do not cause an obvious decrease in body weight or appreciable toxicity, even after their breakdown in vivo. High concentrations of gold nanoparticles induced decreases in body weight, red blood cells, and hematocrit. It was also found that gold nanoparticles administered orally caused significant decreases in body weight, spleen index, and red blood cells. Of the three administration routes, the oral and intraperitoneal routes showed the highest toxicity, and the tail vein injection showed the lowest toxicity. Combining the results of all of these studies, we suggest that targeted gold nanopartices by tail vein injection may be suitable for enhancement of radiotherapy, photothermal therapy, and related medical diagnostic procedures.
Keywords: gold nanoparticles; in vivo; toxicity.
Figures
References
-
- Danieland MC, Astruc D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev. 2004;104:293–346. - PubMed
-
- Eustis S, El-Sayed MA. Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: Noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Hu M, Chen J, Li ZY, et al. Gold nanostructures: Engineering their plasmonic properties for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2006;35:1084–94. - PubMed
-
- Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, van Duyne RP. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater. 2008;7:442–453. - PubMed
-
- Sokolov K, Follen M, Aaron J, et al. Real-time vital optical imaging of precancer using anti-epidermal growth factor receptor anti-bodies conjugated to gold nanoparticles. Cancer Res. 2003;63:1999–2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

