Functional invariant NKT cells in pig lungs regulate the airway hyperreactivity: a potential animal model
- PMID: 21042929
- PMCID: PMC4450678
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-010-9476-4
Functional invariant NKT cells in pig lungs regulate the airway hyperreactivity: a potential animal model
Abstract
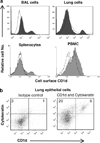
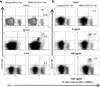
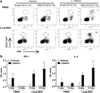
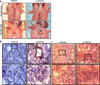
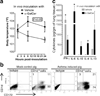
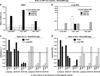
Important roles played by invariant natural killer T (iNKT) cells in asthma pathogenesis have been demonstrated. We identified functional iNKT cells and CD1d molecules in pig lungs. Pig iNKT cells cultured in the presence of α-GalCer proliferated and secreted Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Like in other animal models, direct activation of pig lung iNKT cells using α-GalCer resulted in acute airway hyperreactivity (AHR). Clinically, acute AHR-induced pigs had increased respiratory rate, enhanced mucus secretion in the airways, fever, etc. In addition, we observed petechial hemorrhages, infiltration of CD4(+) cells, and increased Th2 cytokines in AHR-induced pig lungs. Ex vivo proliferated iNKT cells of asthma induced pigs in the presence of C-glycoside analogs of α-GalCer had predominant Th2 phenotype and secreted more of Th2 cytokine, IL-4. Thus, baby pigs may serve as a useful animal model to study iNKT cell-mediated AHR caused by various environmental and microbial CD1d-specific glycolipid antigens.
Figures
References
-
- Ibrahim Z, Busch J, Awwad M, Wagner R, Wells K, Cooper DK. Selected physiologic compatibilities and incompatibilities between human and porcine organ systems. Xenotransplantation. 2006;13(6):488–499. - PubMed
-
- Baskerville A. Development of the early lesions in experimental enzootic pneumonia of pigs: an ultrastructural and histological study. Res Vet Sci. 1972;13(6):570–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

