Development of an image-based system for measurement of membrane potential, intracellular Ca(2+) and contraction in arteriolar smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 21044217
- PMCID: PMC4826593
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2010.00059.x
Development of an image-based system for measurement of membrane potential, intracellular Ca(2+) and contraction in arteriolar smooth muscle cells
Abstract
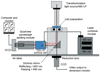
Objective: Changes in smooth muscle cell (SMC) membrane potential (Em) are critical to vasomotor responses. As a fluorescent indicator approach would lessen limitations of glass electrodes in contracting preparations, we aimed to develop a Forster (or fluorescence) resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based measurement for Em.
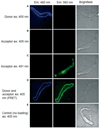
Methods: The FRET pair used in this study (donor CC2-DMPE [excitation 405 nm] and acceptor DisBAC(4) (3)) provide rapid measurements at a sensitivity not achievable with many ratiometric indicators. The method also combined measurement of changes in Ca(2+) (i) using fluo-4 and excitation at 490 nm.
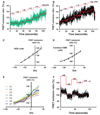
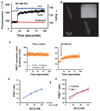
Results: After establishing loading conditions, a linear relationship was demonstrated between Em and fluorescence signal in FRET dye-loaded HEK cells held under voltage clamp. Over the voltage range from -70 to +30 mV, slope (of FRET signal vs. voltage, m) = 0.49 ± 0.07, r(2) = 0.96 ± 0.025. Similar data were obtained in cerebral artery SMCs, slope (m) = 0.30 ± 0.02, r(2) = 0.98 ± 0.02. Change in FRET emission ratio over the holding potential of -70 to +30 mV was 41.7 ± 4.9% for HEK cells and 30.0 ± 2.3% for arterial SMCs. The FRET signal was also shown to be modulated by KCl-induced depolarization in a concentration-dependent manner. Further, in isolated arterial SMCs, KCl-induced depolarization (60 mM) measurements occurred with increased fluo-4 fluorescence emission (62 ± 9%) and contraction (-27 ± 4.2%).
Conclusions: The data support the FRET-based approach for measuring changes in Em in arterial SMCs. Further, image-based measurements of Em can be combined with analysis of temporal changes in Ca(2+) (i) and contraction.
© 2010 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Beach JM, McGahren ED, Xia J, Duling BR. Ratiometric measurement of endothelial depolarization in arterioles with a potential-sensitive dye. Am J Physiol. 1996;270:H2216–2227. - PubMed
-
- Brueggemann LI, Markun DR, Henderson KK, Cribbs LL, Byron KL. Pharmacological and electrophysiological characterization of store-operated currents and capacitative Ca(2+) entry in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;317:488–499. - PubMed
-
- Burgstahler R, Koegel H, Rucker F, Tracey D, Grafe P, Alzheimer C. Confocal ratiometric voltage imaging of cultured human keratinocytes reveals layer-specific responses to ATP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003;284:C944–952. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Rivers RJ. Measurement of membrane potential and intracellular Ca(2+) of arteriolar endothelium and smooth muscle in vivo. Microvasc Res. 2001;62:55–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

