Pro-neurotrophins secreted from retinal ganglion cell axons are necessary for ephrinA-p75NTR-mediated axon guidance
- PMID: 21044296
- PMCID: PMC2987844
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8104-5-30
Pro-neurotrophins secreted from retinal ganglion cell axons are necessary for ephrinA-p75NTR-mediated axon guidance
Abstract
Background: Retinotectal map formation develops via topographically specific guidance and branching of retinal axons in their target area. This process is controlled, in part, by reverse signalling of ephrinAs expressed on retinal axons. As glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored molecules, ephrinAs require transmembrane co-receptors to exert this function, for which the two neurotrophin receptors, p75NTR and TrkB, were recently proposed.
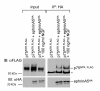
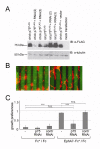
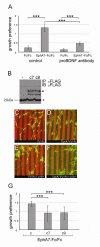
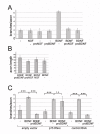
Results: We show here that the ligands for these receptors, the brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor (proBDNF) and its processed form, BDNF, respectively, control the branching of retinal axons antagonistically, which they mediate by inducing the corresponding neurotrophin receptor-ephrinA complexes. Moreover, scavenging proneurotrophins, by adding antibodies specific for the pro-domain of proBNDF or a soluble extracellular domain of p75NTR, abolish repellent ephrinA reverse signalling in the stripe assay.
Conclusions: This indicates that retinal cells secrete proneurotrophins, inducing the ephrinA-p75NTR interaction and enabling repellent axon guidance. The antagonistic functions of proBDNF and BDNF raise the possibility that topographic branching is controlled by local control of processing of proneurotrophins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EphrinA6 on chick retinal axons is a key component for p75(NTR)-dependent axon repulsion and TrkB-dependent axon branching.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jun;47(2):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.03.008. Epub 2011 Apr 2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21463686 Free PMC article.
-
A TrkB/EphrinA interaction controls retinal axon branching and synaptogenesis.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 26;28(48):12700-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1915-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 19036963 Free PMC article.
-
Axonal ephrinA/EphA interactions, and the emergence of order in topographic projections.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012 Feb;23(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.10.015. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22040913 Review.
-
The secreted brain-derived neurotrophic factor precursor pro-BDNF binds to TrkB and p75NTR but not to TrkA or TrkC.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Apr 1;80(1):18-28. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20432. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15704182
-
ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin.J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 1;25(22):5455-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5123-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15930396 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From Neural Crest Development to Cancer and Vice Versa: How p75NTR and (Pro)neurotrophins Could Act on Cell Migration and Invasion?Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Aug 23;11:244. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00244. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30190671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling development in retinal afferents: retinotopy, segregation, and ephrinA/EphA mutants.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 14;9(8):e104670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104670. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25122119 Free PMC article.
-
EphrinA6 on chick retinal axons is a key component for p75(NTR)-dependent axon repulsion and TrkB-dependent axon branching.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jun;47(2):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.03.008. Epub 2011 Apr 2. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21463686 Free PMC article.
-
EphA3 expressed in the chicken tectum stimulates nasal retinal ganglion cell axon growth and is required for retinotectal topographic map formation.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038566. Epub 2012 Jun 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22685584 Free PMC article.
-
PROneurotrophins and CONSequences.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;55(4):2934-2951. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0505-7. Epub 2017 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28456935 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

