Effects of gene therapy on muscle 18S rRNA expression in mouse model of ALS
- PMID: 21044297
- PMCID: PMC2987871
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-3-275
Effects of gene therapy on muscle 18S rRNA expression in mouse model of ALS
Abstract
Background: The efficiency of gene therapy experiments is frequently evaluated by measuring the impact of the treatment on the expression of genes of interest by quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) and by normalizing these values to those of housekeeping (HK) genes constitutively expressed throughout the experiment. The objective of this work was to study the effects of muscle gene therapy on the expression of 18 S ribosomal RNA (Rn18S), a commonly used HK gene.
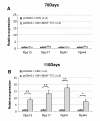
Findings: Mouse model of motor neuron disease (SOD1-G93A) was injected intramuscularly with Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF-TTC) encoding or control naked DNA plasmids. qRT-PCR expression analysis was performed for BDNF and HK genes Rn18 S, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) and β-actin (Actb). We report that elevated BDNF expression in the injected muscle was accompanied with increased Rn18 S expression, whereas Gapdh and Actb were not affected. Increased "ribosomal output" upon BDNF stimulation was supported by increased steady-state levels of ribosomal protein mRNAs.
Conclusions: Ribosomal RNA transcription may be directly stimulated by administration of trophic factors. Caution should be taken in using Rn18 S as a HK gene in experiments where muscle metabolism is likely to be altered by therapeutic intervention.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation and validation of housekeeping genes in response to ionizing radiation and chemical exposure for normalizing RNA expression in real-time PCR.Mutat Res. 2008 Jan 8;649(1-2):126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.08.005. Epub 2007 Aug 19. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 17904413
-
Determination of internal controls for quantitative real time RT-PCR analysis of the effect of Edwardsiella tarda infection on gene expression in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011 Feb;30(2):720-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2010.12.028. Epub 2011 Jan 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21220029
-
Housekeeping while brain's storming Validation of normalizing factors for gene expression studies in a murine model of traumatic brain injury.BMC Mol Biol. 2008 Jul 8;9:62. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-9-62. BMC Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18611280 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring valid reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis in Sesamia inferens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae).PLoS One. 2015 Jan 13;10(1):e0115979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0115979. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25585250 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of reference genes that are independent of feeding rhythms for circadian studies of mouse metabolic tissues.Mol Genet Metab. 2017 Jun;121(2):190-197. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2017.04.001. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Mol Genet Metab. 2017. PMID: 28410879
Cited by
-
Exploring transcriptomic databases to identify and experimentally validate tissue-specific consensus reference gene for gene expression normalization in BALB/c mice acutely exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.Curr Res Toxicol. 2025 Apr 27;8:100234. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2025.100234. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40391131 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: role of stem cells, growth factors, and gene therapy.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2012 Mar;12(1):15-27. doi: 10.2174/187152412800229152. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22283698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Different Approaches for the Selection of Reference Genes in RT-qPCR Experiments: A Case Study in Skeletal Muscle of Growing Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 16;18(5):1060. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051060. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28509880 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5245–5250. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

