Ovine serum biomarkers of early and late phase scrapie
- PMID: 21044301
- PMCID: PMC2988006
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-6148-6-49
Ovine serum biomarkers of early and late phase scrapie
Abstract
Background: Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies are fatal neurodegenerative disease occurring in animals and humans for which no ante-mortem diagnostic test in biological fluids is available. In such pathologies, detection of the pathological form of the prion protein (i.e., the causative factor) in blood is difficult and therefore identification of new biomarkers implicated in the pathway of prion infection is relevant.
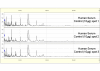
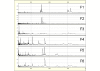
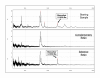
Methods: In this study we used the SELDI-TOF MS technology to analyze a large number of serum samples from control sheep and animals with early phase or late phase scrapie. A few potential low molecular weight biomarkers were selected by statistical methods and, after a training analysis, a protein signature pattern, which discriminates between early phase scrapie samples and control sera was identified.
Results: The combination of early phase biomarkers showed a sensitivity of 87% and specificity of 90% for all studied sheep in the early stage of the disease. One of these potential biomarkers was identified and validated in a SELDI-TOF MS kinetic study of sera from Syrian hamsters infected by scrapie, by western blot analysis and ELISA quantitation.
Conclusions: Differential protein expression profiling allows establishing a TSE diagnostic in scrapie sheep, in the early phase of the disease. Some proteic differences observed in scrapie sheep exist in infected hamsters. Further studies are being performed to identify all the discriminant biomarkers of interest and to test our potential markers in a new cohort of animals.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Investigation of serum protein profiles in scrapie infected sheep by means of SELDI-TOF-MS and multivariate data analysis.BMC Res Notes. 2013 Nov 14;6:466. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-6-466. BMC Res Notes. 2013. PMID: 24229425 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic microparticle-based multimer detection system for the detection of prion oligomers in sheep.Int J Nanomedicine. 2015 Sep 9;10(Spec Iss):241-50. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S88377. eCollection 2015. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015. PMID: 26425091 Free PMC article.
-
Western blot mapping of disease-specific amyloid in various animal species and humans with transmissible spongiform encephalopathies using a high-yield purification method.J Gen Virol. 1995 Oct;76 ( Pt 10):2567-76. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-76-10-2567. J Gen Virol. 1995. PMID: 7595360
-
Prion encephalopathies of animals and humans.Dev Biol Stand. 1993;80:31-44. Dev Biol Stand. 1993. PMID: 8270114 Review.
-
The use of non-prion biomarkers for the diagnosis of Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies in the live animal.Vet Res. 2005 Sep-Dec;36(5-6):665-83. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2005028. Vet Res. 2005. PMID: 16120244 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of selected genes isolated from whole blood, liver and obex in lambs with experimental classical scrapie and healthy controls, showing a systemic innate immune response at the clinical end-stage.BMC Vet Res. 2018 Sep 12;14(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1607-9. BMC Vet Res. 2018. PMID: 30208891 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of an acute phase response in sheep with clinical classical scrapie.BMC Vet Res. 2012 Jul 17;8:113. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-8-113. BMC Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 22805457 Free PMC article.
-
Applying the tools of chemistry (mass spectrometry and covalent modification by small molecule reagents) to the detection of prions and the study of their structure.Prion. 2014 Jan-Feb;8(1):42-50. doi: 10.4161/pri.27891. Prion. 2014. PMID: 24509645 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical Inference for Box-Cox based Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves.Stat Med. 2024 Dec 30;43(30):6099-6122. doi: 10.1002/sim.10252. Epub 2024 Nov 17. Stat Med. 2024. PMID: 39551723
-
Characterisation of the circulating acellular proteome of healthy sheep using LC-MS/MS-based proteomics analysis of serum.Proteome Sci. 2017 Jun 10;15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12953-017-0119-z. eCollection 2016. Proteome Sci. 2017. PMID: 28615994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smits MA, Bossers A, Schreuder BE. Prion protein and scrapie susceptibility. Vet Q. 1997;19(3):101–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

