Evaluation of six CTLA-4 polymorphisms in high-risk melanoma patients receiving adjuvant interferon therapy in the He13A/98 multicenter trial
- PMID: 21044351
- PMCID: PMC2988721
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-108
Evaluation of six CTLA-4 polymorphisms in high-risk melanoma patients receiving adjuvant interferon therapy in the He13A/98 multicenter trial
Abstract
Purpose: Interferon is approved for adjuvant treatment of patients with stage IIb/III melanoma. The toxicity and uncertainty regarding survival benefits of interferon have qualified its acceptance, despite significant durable relapse prevention in a fraction of patients. Predictive biomarkers that would enable selection of patients for therapy would have a large impact upon clinical practice. Specific CTLA-4 polymorphisms have previously shown an association with response to CTLA-4 blockade in patients with metastatic melanoma and the development of autoimmunity.
Experimental design: 286 melanoma patients and 288 healthy controls were genotyped for six CTLA-4 polymorphisms previously suggested to be important (AG 49, CT 318, CT 60, JO 27, JO30 and JO 31). Specific allele frequencies were compared between the healthy and patient populations, as well as presence or absence of these in relation to recurrence. Alleles related to autoimmune disease were also investigated.
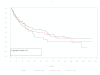
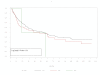
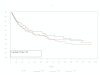
Results: No significant differences were found between the distributions of CTLA-4 polymorphisms in the melanoma population compared with healthy controls. Relapse free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) did not differ significantly between patients with the alleles represented by these polymorphisms. No correlation between autoimmunity and specific alleles was shown. The six polymorphisms evaluated where strongly associated (Fisher's exact p-values < 0.001 for all associations) and significant linkage disequilibrium among these was indicated.
Conclusion: No polymorphisms of CTLA-4 defined by the SNPs studied were correlated with improved RFS, OS, or autoimmunity in this high-risk group of melanoma patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new mathematical model for the interpretation of translational research evaluating six CTLA-4 polymorphisms in high-risk melanoma patients receiving adjuvant interferon.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86375. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086375. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475110 Free PMC article.
-
A novel multiplex pyrosequencing assay for genotyping functionally relevant CTLA-4 polymorphisms: potential applications in autoimmunity and cancer.Hum Immunol. 2014 Aug;75(8):730-9. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.04.019. Epub 2014 May 5. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24801647
-
Association of CTLA-4 polymorphisms with improved overall survival in melanoma patients treated with CTLA-4 blockade: a pilot study.Cancer Invest. 2013 Jun;31(5):336-45. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2013.793699. Epub 2013 May 3. Cancer Invest. 2013. PMID: 23641913
-
Anti-CTLA-4 antibody adjuvant therapy in melanoma.Semin Oncol. 2010 Oct;37(5):455-9. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.09.009. Semin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21074060 Review.
-
CTLA-4 blockade with monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic cancer: surgical issues.Ann Surg Oncol. 2008 Nov;15(11):3014-21. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-0104-y. Epub 2008 Aug 21. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18716842 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of Research on Germline Genetic Variation in Immune Genes and Cancer Outcomes.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022 Mar 1;31(3):495-506. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-21-0583. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2022. PMID: 35027433 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen-4 as a new therapeutic approach for advanced melanoma.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 Dec;12(17):2695-706. doi: 10.1517/14656566.2011.629187. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011. PMID: 22077831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new mathematical model for the interpretation of translational research evaluating six CTLA-4 polymorphisms in high-risk melanoma patients receiving adjuvant interferon.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86375. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086375. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475110 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of polymorphism, hypermethylation and expression pattern of CTLA4 gene in a sample of Iranian patients with schizophrenia.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Aug;40(8):5123-8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2614-3. Epub 2013 May 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23666060
-
A multi-factorial genetic model for prognostic assessment of high risk melanoma patients receiving adjuvant interferon.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040805. Epub 2012 Jul 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, Borden EC, Blum RH. Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma: the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:7–17. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sosman JA, Sondak VK, Agarwala SS, Ernstoff MS, Rao U. High-dose interferon alfa-2b significantly prolongs relapse-free and overall survival compared with the GM2 KLH/QS 21 vaccine in patients with resected stage IIB-III melanoma: results of intergroup trial E1694/S9512/C509801. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2370–80. - PubMed
-
- Kirkwood JM, Richards Th, Zarour HM, Sosman J, Ernstoff M, Whiteside TL, Ibrahim J, Blum R, Wieand S, Mascari R. Immunomodulatory effects of high-dose and low-dose interferon a2b in patients with high-risk resected melanoma. The E2690 laboratory corollary of intergroup adjuvant trial E 1690. Cancer. 2002;95:1101–1112. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10775. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atkins MB, Mier JW, Parkinson DP, Gould JA, Berkman EM, Kaplan MM. Hypothyroidism after treatment with interleukin-2 and lymphokine-activated killer cells. N Engl J Med. 1988;318:1557–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical