Real-time, high-throughput measurements of peptide-MHC-I dissociation using a scintillation proximity assay
- PMID: 21044632
- PMCID: PMC4341823
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.10.012
Real-time, high-throughput measurements of peptide-MHC-I dissociation using a scintillation proximity assay
Abstract
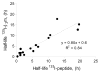
Efficient presentation of peptide-MHC class I complexes to immune T cells depends upon stable peptide-MHC class I interactions. Theoretically, determining the rate of dissociation of a peptide-MHC class I complexes is straightforward; in practical terms, however, generating the accurate and closely timed data needed to determine the rate of dissociation is not simple. Ideally, one should use a homogenous assay involving an inexhaustible and label-free assay principle. Here, we present a homogenous, high-throughput peptide-MHC class I dissociation assay, which by and large fulfill these ideal requirements. To avoid labeling of the highly variable peptide, we labeled the invariant β2m and monitored its dissociation by a scintillation proximity assay, which has no separation steps and allows for real-time quantitative measurement of dissociation. Validating this work-around to create a virtually label-free assay, we showed that rates of peptide-MHC class I dissociation measured in this assay correlated well with rates of dissociation rates measured conventionally with labeled peptides. This assay can be used to measure the stability of any peptide-MHC class I combination, it is reproducible and it is well suited for high-throughput screening. To exemplify this, we screened a panel of 384 high-affinity peptides binding to the MHC class I molecule, HLA-A*02:01, and observed the rates of dissociation that ranged from 0.1h to 46h depending on the peptide used.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The influence of exogenous peptide on beta2-microglobulin exchange in the HLA complex: analysis in real-time.Immunogenetics. 1998 Jul;48(2):98-107. doi: 10.1007/s002510050409. Immunogenetics. 1998. PMID: 9634473
-
Assembly and dissociation of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-A2 studied by real-time fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Biochemistry. 2000 Sep 12;39(36):11163-9. doi: 10.1021/bi000763z. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10998256
-
The beta 2-microglobulin dissociation rate is an accurate measure of the stability of MHC class I heterotrimers and depends on which peptide is bound.J Immunol. 1992 Sep 15;149(6):1896-904. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1517560
-
MHC class I/peptide interactions: binding specificity and kinetics.J Mol Recognit. 1993 Jun;6(2):59-69. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300060204. J Mol Recognit. 1993. PMID: 8305252 Review.
-
Class I MHC-peptide interaction: structural and functional aspects.Behring Inst Mitt. 1994 Jul;(94):48-60. Behring Inst Mitt. 1994. PMID: 7998914 Review.
Cited by
-
Current tools for predicting cancer-specific T cell immunity.Oncoimmunology. 2016 Apr 25;5(7):e1177691. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1177691. eCollection 2016 Jul. Oncoimmunology. 2016. PMID: 27622028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NetMHCstab - predicting stability of peptide-MHC-I complexes; impacts for cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope discovery.Immunology. 2014 Jan;141(1):18-26. doi: 10.1111/imm.12160. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 23927693 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of MHC/peptide interactions by gel filtration or monoclonal antibody capture.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2013 Feb;Chapter 18:Unit 18.3.. doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im1803s100. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23392640 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 adaptation to NK cell-mediated immune pressure.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 5;13(6):e1006361. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006361. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28582449 Free PMC article.
-
NNAlign_MA; MHC Peptidome Deconvolution for Accurate MHC Binding Motif Characterization and Improved T-cell Epitope Predictions.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Dec;18(12):2459-2477. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR119.001658. Epub 2019 Oct 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 31578220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assarsson E, Sidney J, Oseroff C, Pasquetto V, Bui HH, Frahm N, Brander C, Peters B, Grey H, Sette A. A quantitative analysis of the variables affecting the repertoire of T cell specificities recognized after vaccinia virus infection. J Immunol. 2007;178:7890–901. - PubMed
-
- Binz AK, Rodriguez RC, Biddison WE, Baker BM. Thermodynamic and kinetic analysis of a peptide-class I MHC interaction highlights the noncovalent nature and conformational dynamics of the class I heterotrimer. Biochemistry. 2003;42:4954–61. - PubMed
-
- Bosworth N, Towers P. Scintillation proximity assay. Nature. 1989;341:167–8. - PubMed
-
- Buchli R, VanGundy RS, Hickman-Miller HD, Giberson CF, Bardet W, Hildebrand WH. Real-time measurement of in vitro peptide binding to soluble HLA-A*0201 by fluorescence polarization. Biochemistry. 2004;43:14852–63. - PubMed
-
- Buchli R, VanGundy RS, Hickman-Miller HD, Giberson CF, Bardet W, Hildebrand WH. Development and validation of a fluorescence polarization-based competitive peptide-binding assay for HLA-A*0201--a new tool for epitope discovery. Biochemistry. 2005;44:12491–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

